COMPLETING THE SQUARE PRACTICE WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Solve the following quadratic equations by completing the square
(i) x2+6x–7 = 0
(ii) x2+3x+1 = 0
(iii) 2x2+5x-3 = 0
(iv) 4x2+4bx–(a2-b2) = 0
(v) (5x+7)/(x–1) = 3x+2
Solution
Question 1 :
x2+6x–7 = 0
Solution :
x2+6x–7 = 0
Step 1 :
Notice that the coefficient of x2 is 1, so don't have to divide the entire equation by any numerical value.
Step 2 :
Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2.
x2+2⋅x⋅3 –7 = 0
Step 3 :
Here the first and second term is in the form a2 + 2ab, in order to complete this formula, we need b2.
Here b = 3
x2+2⋅x⋅3+32-32 –7 = 0
(x+3)2–9–7 = 0
(x+3)2–16 = 0
(x+3)2 = 16
(x+3) = √16
x+3 = ±4
|
x+3 = 4 x = 1 |
x+3 = -4 x = -7 |
Question 2 :
x2+3x+1 = 0
Solution :
Step 1 :
Notice that the coefficient of x2 is 1, so don't have to divide the entire equation by any numerical value.
Step 2 :
Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2.
x2+2⋅x⋅(3/2)+1 = 0
Step 3 :
Here the first and second term is in the form a2 + 2ab, in order to complete this formula, we need b2.
Here b = 3
x22⋅x⋅(3/2)+(3/2)2-(3/2)2+1 = 0
[x + (3/2)]2 – (9/4) + 1 = 0
[x+(3/2)]2 = (9/4) – 1
[x+(3/2)]2 = 5/4
x+(3/2) = √(5/4)
[x+(3/2)] = ±√5/2
|
x+(3/2) = √5/2 x = (√5-3)/2 |
x+(3/2) = -√5/2 x = (-√5-3)/2 |
So, the solution is {(√5-3)/2, (-√5-3)/2}.
Question 3 :
2x2+5x-3 = 0
Solution :
Step 1 :
Notice that the coefficient of x2 is 2, so divide the entire equation by 2.
x2+(5x/2)-(3/2) = 0
Step 2 :
Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2.
x2+2⋅x⋅(3/2)+1 = 0
Step 3 :
Here the first and second term is in the form a2 + 2ab, in order to complete this formula, we need b2.
Here b = 3
2x² + 5x - 3 = 0
Now we are going to divide the whole equation by 2
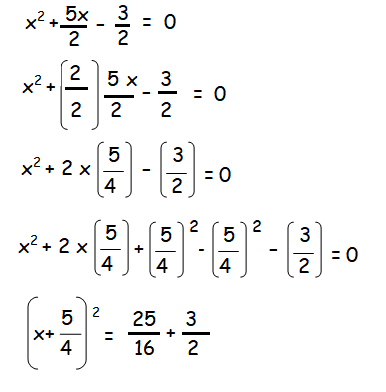
(x+5/4)2 = 49/16
(x+5/4) = √49/16
(x+5/4) = ±7/4
|
x+5/4 = 7/4 x = 2/4 x = 1/2 |
x+5/4 = -7/4 x = -12/4 x = -3 |
So, the solution is {-3, 1/2}.
Question 4 :
4x2+4bx–(a2 - b2) = 0
Solution :
4x2+4bx–(a2 - b2) = 0
Now we are going to divide the whole equation by 4
x2+bx–[(a2 - b2)/4] = 0
x2+2(x)(b/2)+(b/2)2–(b/2)2 – [(a2 - b2)/4] = 0
[x + (b/2)]2 – (b2/4) – [(a2-b2)/4] = 0
[x + (b/2)]2 = (b2/4)+[(a2-b2)/4]
[x + (b/2)]2 = [(b2+a2-b2)/4]
[x + (b/2)]2 = a2/4
[x + (b/2)] = √(a²/4)
[x + (b/2)] = ±(a/2)
|
x + (b/2) = a/2 x = (a-b)/2 |
x + (b/2) = -a/2 x = (-a-b)/2 |
So, the solution is {(a-b)/2, (-a-b)/2}.
Question 5 :
(5x+7)/(x–1) = 3x+2
Solution :
(5x+7) = (3x+2)(x–1)
5x+7 = 3x2–x–2
3x2–x–5x–7-2 = 0
3x2–6x–9 = 0
x2–2x–3 = 0
(x–3)(x+1) = 0
|
x-3 = 0 x = 3 |
x+1 = 0 x = -1 |
So, the solution is {-1, 3}.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


