DE MORGANS LAWS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
De Morgan’s laws relate the three basic set operations Union, Intersection and Complement.
De Morgan's First Law :
The complement of the union of two sets is equal to the intersection of their complements.
That is,
(AuB)' = A'nB'
De Morgan's Second Law :
The complement of the intersection of two sets is equal to the union of their complements.
That is,
(AnB)' = A'uB'
De Morgan's First Law - Proof by Venn diagram
(AuB)' = A'nB'
Let's draw Venn diagram for (AuB)'.
To draw Venn diagram for (AuB)', first draw Venn diagram for (AuB).
To draw Venn diagram for (AuB)', shade the region other than (AuB).
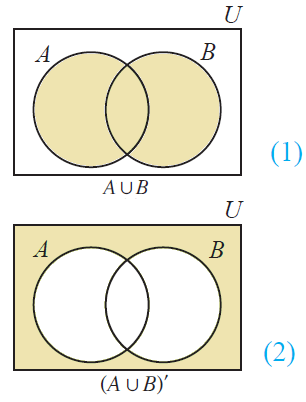
Now, let's draw Venn diagram for (A'n B').
Draw Venn diagram for A' and B'.
Then, to draw Venn diagram for (A'nB'), find the common region of A' and B'.
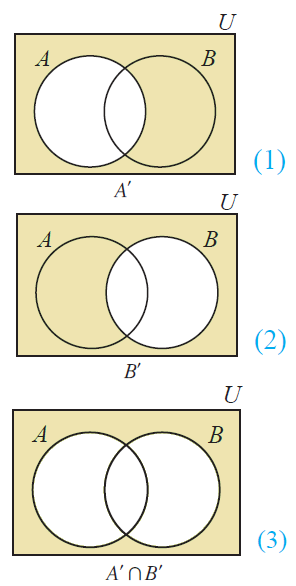
The resulting Venn diagrams of (AuB)' and (A'nB') are same.
So,
(AuB)' = A'nB'
De Morgan's First Law - Proof by Venn diagram
(AnB)' = A'uB'
Let's draw Venn diagram for (AnB).
To draw Venn diagram for (AnB)', first draw Venn diagram for (AnB)
To draw Venn diagram for (AnB)', shade the region other than (AnB).
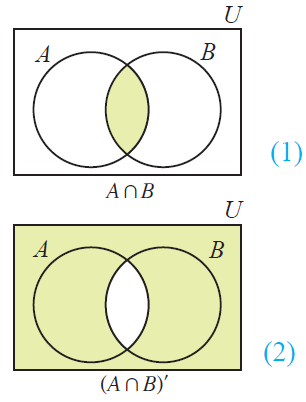
Now, let's draw Venn diagram for (A'u B').
Draw Venn diagram for A' and B'.
Then, to draw Venn diagram for (A'uB'), join A' and B'.
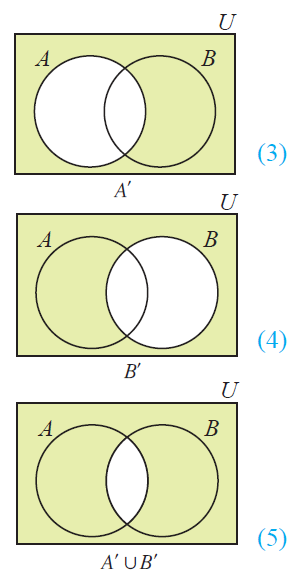
The resulting Venn diagrams of (AnB)' and (A'uB') are same.
So,
(AnB)' = A'uB'
Problem 1 :
Two finite sets A and B that n(A) = 3 and n(B) = 6. Then minimum number of numbers of elements in A U B
a) 3 b) 6 c) 9 d) 18
Solution :
n(A) = 3 and n(B) = 6
From this, we understand that the set A has 3 elements and set B has 6 elements.
The set A U B consist of all the elements in set A and B. We may have 3 same elements in both sets A and B. In this case, since we are not allowed to repeat the elements so we have 6 elements in the set A U B.
Problem 2 :
State De-Morgan's law and justify it for following sets
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
A = {2, 4, 6, 8}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
Solution :
i) (A U B)' = A' n B'
ii) (A n B)' = A' U B'
i)
AUB = {2, 4, 6, 8} U {3, 4, 5, 6}
= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8}
(AUB)' = {1, 7, 9} -----(1)
A' = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
B' = {1, 2, 7, 8, 9}
A' n B' = {1, 7, 9} -----(2)
(1) = (2)
ii)
AnB = {2, 4, 6, 8} n {3, 4, 5, 6}
= {4, 6}
(AnB)' = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9} -----(1)
A' = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
B' = {1, 2, 7, 8, 9}
A' u B' = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9} -----(2)
Problem 3 :
Let A = {a, b, c, d, e}, B = {a, c, e, g} and C = {b, e, f, g}
Verify the following.
i) A n (B - C) = (A n B) - (A n C)
ii) A - (B U C) = (A - B) n (A - C)
Solution :
i) A - (B - C) = (A n B) - (A n C)
B - C = {a, c, e, g} - {b, e, f, g}
Leave the common elements of B and C, then write the remaining elements in B.
= {a, c}
A n (B - C) = {a, b, c, d, e} n {a, c}
Leave the common elements in these two sets and write the remaining elements in A.
A n (B - C) = {a, c} ----(1)
(A n B) = {a, b, c, d, e} n {a, c, e, g}
= {a, c, e}
(A n C) = {a, b, c, d, e} n {b, e, f, g}
= {b, e}
(A n B) - (A n C) = {a, c, e} - {b, e}
(A n B) - (A n C) = {a, c} ----(2)
(1) = (2)
ii) A - (B U C) = (A - B) n (A - C)
B U C = {a, c, e, g} U {b, e, f, g}
= {a, b, c, e, f, g}
A - (B U C) = {a, b, c, d, e} - {a, b, c, e, f, g}
= {d} -------(1)
(A - B) = {a, b, c, d, e} - {a, c, e, g}
= {b, d}
(A - C) = {a, b, c, d, e} - {b, e, f, g}
= {a, c, d}
(A n B) n (A n C) = {b, d} n {a, c, d}
(A n B) n (A n C) = {d} ----(2)
(1) = (2)
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


