DE MORGANS LAW FOR COMPLIMENTS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
De Morgan’s father (a British national) was in the service of East India Company, India. Augustus De Morgan (1806-1871) was born in Madurai, Tamilnadu, India. His family moved to England when he was seven months old. He had his education at Trinity college, Cambridge, England.
De Morgan’s laws relate the three basic set operations union, intersection and complement.
De morgan's law for set complementation :
Let U be the universal set containing sets A and B. Then
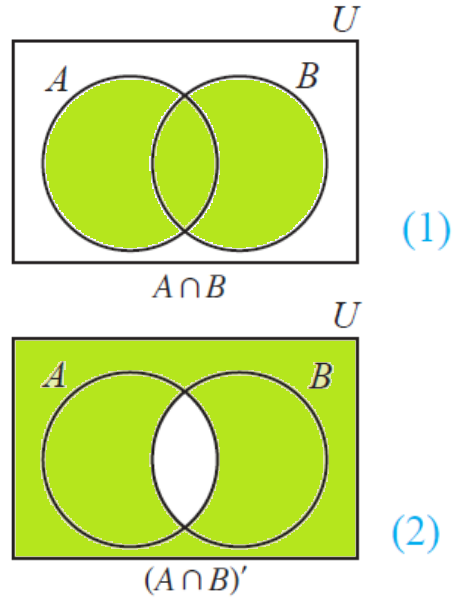
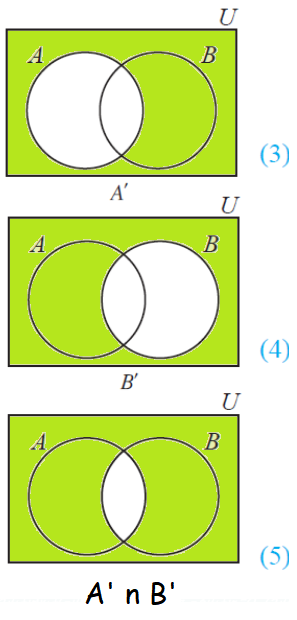
(i) (A u B)' = A' n B'
(ii) (A n B)' = A' u B'
Proof by Venn diagram
(A n B)' = A' u B'
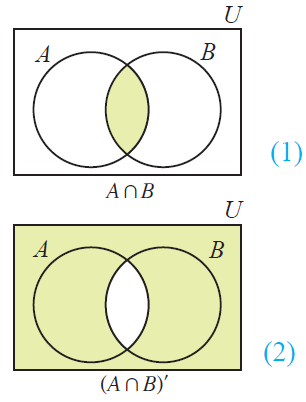
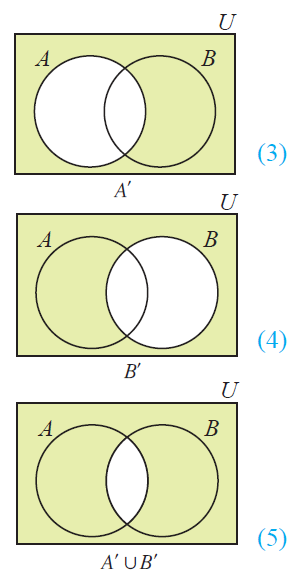
From the above Venn diagrams (2) and (5), it is clear that
(A n B)' = A' u B'
Hence, De morgan's law for complementation is verified.
(A U B)' = A' n B'
Solved Examples
Example 1 :
Let U = {-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, .......10 }, A = {-2, 2, 3, 4, 5} and B = {1, 3, 5, 8, 9}. Verify De Morgan’s laws of complementation
Solution :
First, we shall verify (A u B)' = A' n B'
To do this, we consider
A u B = {-2, 2, 3, 4, 5} u {1, 3, 5, 8, 9}
A u B = {-2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9}
We know that
(A u B)' = U \ {-2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9}
(A u B)' = {-1, 0, 6, 7, 10} -----(1)
A' = U \ A = U \ { -2, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
= {-1, 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
B' = U \ B = U \ {1, 3, 5, 8, 9}
= {-2, -1, 0, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10}
A'nB' = {-1, 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} n {-2, -1, 0, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10}
A' n B' = {-1, 0, 6, 7, 10} -----(2)
From (1) and (2), it is clear that (A u B)' = A' n B'
First, we shall verify (A n B)' = A'u B'.
To do this, we consider
A n B = {- 2, 2, 3, 4, 5 } u {1, 3, 5, 8, 9}
A n B = {3, 5}
We know that
(A n B)' = U \ { 3, 5 }
(A n B)' = {2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
A' = U \ A = U \ {-2, 2, 3, 4, 5}
= {-1, 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
B' = U \ B = U \ {1, 3, 5, 8, 9}
= {-2, -1, 0, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10}
A'UB' = {-1, 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} n {-2, -1, 0, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10}
A' U B' = {2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} -----(2)
From (1) and (2), it is clear that
(A n B)' = A' U B'
Example 2 :
Let U = {4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28} , A = {8, 16, 24} and B = {4, 16, 20, 28}. Find (AU B)' and (A n B)'.
Solution :
A u B = {8, 16, 24} U {4, 16, 20, 28}
A u B = { 4, 8, 16, 20, 24, 28 }
We know that
(A u B)' = U \ { 4, 8, 16, 20, 24, 28 }
(A u B)' = { 12 }
(A n B) = {8, 16, 24} n {4, 16, 20, 28}
= {16}
(A n B)' = U \ { 16 }
= {4, 8, 12, 20, 24, 28}
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


