DE MOIVRE'S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Theorem :
For any complex number cos θ + i sin θ and any integer n,
(cos θ + i sin θ)n = cos nθ + i sin nθ
Corollary :
(cos θ - i sin θ)n = cos nθ - i sin nθ
(cos θ + i sin θ)-n = cos nθ - i sin nθ
(cos θ - i sin θ)-n = cos nθ + i sin nθ
Solved Problems
Problem 1 :
Simplify :
Solution :
Problem 2 :
Simplify :
Solution :
Problem 3 :
If z = cos θ + i sin θ, find
Solution :
Part (i) :
Part (ii) :
Problem 4 :
Simplify :
Solution :
Let z = cos 2θ + i sin 2θ. Then
For any complex number z, if |z| = 1, then
Problem 5 :
Simplify :
Solution :
Problem 6 :
Simplify :
(1 + i)18
Solution :
Write the givcen complex number in polar form.
(1 + i)18 = r(cos θ + i sin θ)
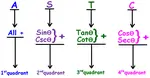
The point on the Argand plane corresponding to the complex number (1 + i) is (1, 1).
And the point (1, 1) lies in the first quadrant.
In the first quadrant,
Writing the given complex number in polar form,
Raising to the power of 18 on both sides,
Problem 7 :
Simplify :
(-√3 + 3i)31
Solution :
Write the givcen complex number in polar form.
(-√3 + 3i)31 = r(cos θ + i sin θ)
The point on the Argand plane corresponding to the complex number (-√3 + 3i) is (-√3, 3).
And the point (-√3, 3) lies in the second quadrant.
In the second quadrant,
Writing the given complex number in polar form,
Raising to the power of 31 on both sides,
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40)
Dec 25, 25 08:30 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41)
Dec 24, 25 07:58 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41) -
ASTC Formula in Trigonometry
Dec 23, 25 11:34 PM
ASTC Formula in Trigonometry - Concepts - Examples and Solved Problems