CONSTANT SPEED
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Constant speed is also called as uniform rate which involves something travelling at fixed and steady pace or else moving at some average speed.
For example, A car travels 3 hours. It travels 30 miles in the first hour, 45 miles in the second hour and 75 miles in the third hour.
speed in the first hour = 30 miles/hour
speed in the second hour = 45 miles/hour
speed in the third hour = 75 miles/hour
We have three different speeds in the three hour journey.
If we want to find the constant speed for the whole journey of three hours, we have to find the ratio between the total distance covered and total time taken.
That is, constant speed = (30 + 45 + 75)/3
= 150/3
= 50 miles/hr
Based on the above example, the formula is to find the constant speed is given below.
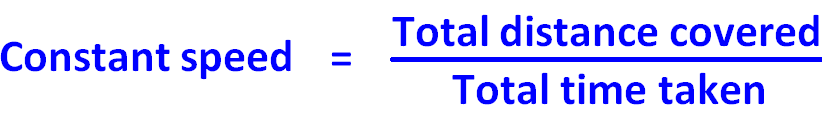
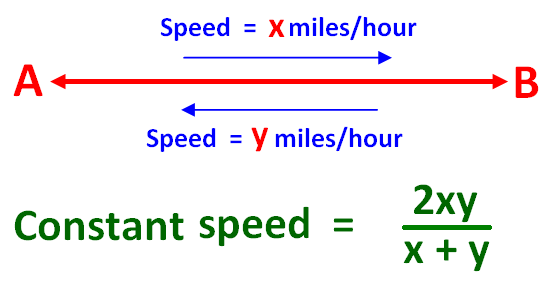
If a person travels from A to B at some speed, say 'x' miles per hour. He comes back from B to A at different speed, say 'y' miles per hour. Both the ways, he covers the same distance, but at different speeds.
Then, the formula is to find the constant speed for the whole journey is given below.
Example 1 :
David drove for 3 hours at a rate of 50 miles per hour, for 2 hours at 60 miles per hour and for 4 hours at a rate of 70 miles per hour. What was his constant-speed for the whole journey ?
Solution :
Step 1 :
Formula for constant speed :
= Total distance/Total time taken
And also, for distance = Rate ⋅ Time
Step 2 :
Distance covered in the first 3 hours :
= 50 ⋅ 3
= 150 miles
Distance covered in the next 2 hours :
= 60 ⋅ 2
= 120 miles
Distance covered in the last 4 hours :
= 70 ⋅ 5
= 350 miles
Step 3 :
Then, total distance is
= 150 + 120 + 350
= 620 miles
Total time is
= 3 + 2 + 5
= 10 hours
Step 4 :
So, constant speed is
= 620/10
= 62 miles per hour
Example 2 :
A person travels from Newyork to Washington at the rate of 45 miles per hour and comes backs to the Newyork at the rate of 55 miles per hour. What is the constant speed for the whole journey ?
Answer :
Step 1 :
Here, both the ways, he covers the same distance.
Then, the formula to find average speed is
= 2xy/(x + y)
Step 2 :
x ----> Rate at which he travels from Newyork to Washington
x = 45
y ----> Rate at which he travels from Newyork to Washington
y = 55
Step 3 :
So, the average speed is
= (2 ⋅ 45 ⋅ 55)/(45 + 55)
= 4950/100
= 49.5
So, the constant speed for the whole journey is 45 miles per hour.
Example 3 :
A man takes 10 hours to go to a place and come back by walking both the ways. He could have gained 2 hours by riding both the ways. The distance covered in the whole journey is 18 miles. Find the constant speed for the whole journey if he goes by walking and comes back by riding.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Given : A man takes 10 hours to go to a place and come back by walking both the ways.
Walking + Walking = 10 hours
2 ⋅ Walking = 10 hours
Walking = 5 hours
Given : He could have gained 2 hours by riding both the ways.
Riding + Riding = 8 hours
2 ⋅ Riding = 8 hours
Riding = 4 hours
Step 2 :
If he goes by walking and comes back by riding, time taken by him :
Walking + Riding = 5 + 4
Walking + Riding = 9 hours
Step 3 :
Total time taken = 9 hours
Total distance covered = 18 miles
Step 4 :
So, the average speed is
= Total distance/Total time
= 18/9
= 2
So, the required constant speed is 2 miles per hour.
Example 4 :
Lily takes 3 hours to travel from place A to place B at the rate of 60 miles per hour. She takes 2 hours to travel from place B to C with 50% increased speed. Find the constant-speed from place A to C.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Speed (from A to B) = 60 miles/hour
Speed (from B to C) = 90 miles/hour (50% increased)
Step 2 :
Formula to find distance is
= Rate ⋅ Time
Distance from A to B is
= 60 ⋅ 3
= 180 miles
Distance from B to C
= 90 ⋅ 2
= 180 miles
Total distance traveled from A to B is
= 180 + 180
= 360 miles
Total time taken from A to B is
= 3 + 2
= 5 hours
Step 3 :
Formula to find average speed is
= Total distance/Total time
= 360/5
= 72
So, the constant speed from place A to B is 72 miles/hour.
Example 5 :
A person takes 5 hours to travel from place A to place B at the rate of 40 miles per hour. He comes back from place B to place A with 25% increased speed. Find the constant speed for the whole journey.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Speed (from A to B) = 40 miles/hour
Speed (from B to A) = 50 miles/hour (25% increased)
Step 2 :
The distance traveled in both the ways (A to B and B to A) is same.
So, the formula to find average distance is
= 2xy/(x + y)
Step 3 :
x ----> Speed from place A to B
x = 40
y ----> Speed from place B to A
y = 50
Step 4 :
Average speed = (2 ⋅ 40 ⋅ 50) / (40 + 50)
= 44.44
So, the constant speed for the whole journey is about 44.44 miles/hour.
Example 6 :
Distance from A to B = 200 miles
Distance from B to C = 300 miles
Distance from C to D = 540 miles
The speed from B to C is 50% more than A to B. The speed from C to D is 50% more than B to C. If the speed from A to B is 40 miles per hour, find the constant speed from A to D.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Speed (from A to B) = 40 miles/hour
Speed (from B to C) = 60 miles/hour (50% more)
Speed (from C to D) = 90 miles/hour (50% more)
Step 2 :
Formula to find time is
= Distance/Time
Time (A to B) = 200/40 = 5 hours
Time (B to C) = 300/60 = 5 hours
Time (C to D) = 540/90 = 6 hours
Total time taken from A to D is
= 5 + 5 + 6
= 16 hours
Total distance from A to D is
= 200 + 300 + 540
= 1040 miles
Step 3 :
Formula to find average speed is
= Total distance/Total time
= 1040/16
= 65
So, the constant speed from A to D is 65 miles per hour.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 41)
Mar 04, 26 04:23 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 41) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40)
Mar 03, 26 06:53 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39)
Mar 03, 26 04:59 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39)