CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
In compound probability of 2 events A and B, we may face the following situation.
That is, if the occurrence of one event, say B, is influenced by the occurrence of another event A, then the two events A and B are known as dependent events.
Joint Probability of the events A and B is denoted by P(AnB).
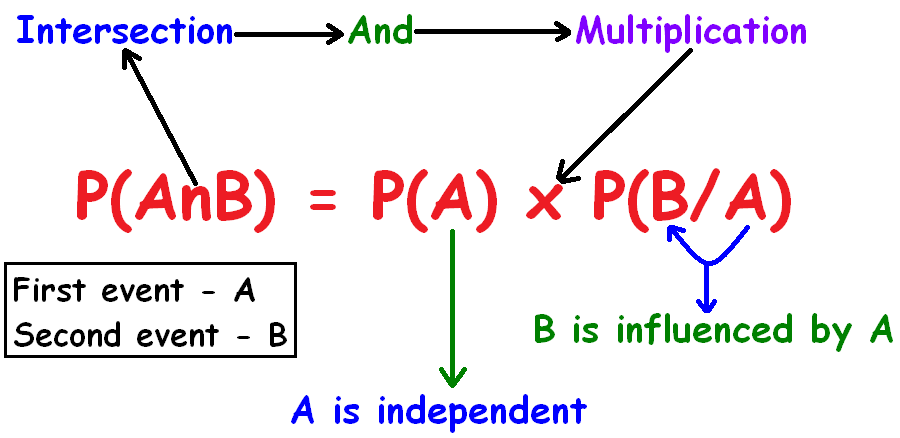
The formula to find P(AnB) is given by
P(AnB) = P(A) x P(B/A)
The above formula has been clearly illustrated in the picture given below.
We use the notation P(B/A), to be read as 'probability of the event B given that the event A has already occurred (or 'the conditional probability of B given A) to suggest that another event B will happen if and only if the first event A has already happened.
This is given by
Provided P(A) > 0 i.e. A is not an impossible event.
Similarly,P(A/B) = P(AnB)/P(B).
Let A, B and C be the three events in the following order of occurrence.
A - 1 st event (Independent)
B - 2 nd event (Influenced by A)
C - 3 rd event (Influenced by both A and B)
Then, the formula to find P(AnBnC) is given by
Example :
If a box contains 5 red and 8 white balls and two successive draws of 2 balls are made from it without replacement, then the probability of the event 'the second draw would result in 2 white balls given that the first draw has resulted in 2 Red balls' is an example of conditional probability.
Since the drawings are made without replacement, the composition of the balls in the box changes and the occurrence of 2 white balls (W2) in the second draw is dependent on the outcome of the first draw (R2).
This event may b denoted by
P(W2/R2)
Solved Problems
Problem 1 :
A pair of dice is thrown together and the sum of points of the two dice is noted to be 10. What is the probability that one of the two dice has shown the point 4?
Solution :
Here, the condition is "The sum of points of the two dice is noted to be 10".
When a pair of dice is thrown together, n(S) = 36.
Let A be the event of getting sum of the points to be 10.
Then, A = {(4, 6), (5, 5), (6, 4)}.
n(A) = 3
P(A) = n(A)/n(S)
= 3/36
= 1/12
Let B be the event of getting 4 on one of the dice.
Then,
B = {(1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 4), (6, 4)}
AnB = {(4, 6), (6, 4)} ----> n(AnB) = 2
P(AnB) = n(AnB)/n(S)
= 2/36
= 1/18
Probability that one of the two dice has shown the point 4 with the condition "sum of points of the two dice to be 10" is
P(B/A) = P(AnB)/P(A)
= (1/18)/(1/12)
= (1/18) x (12/1)
= (1x12)/(18x1)
= 12/18
= 2/3
Problem 2 :
In a group of 20 males and 15 females, 12 males and 8 females are service holders. What is the probability that a person selected at random from the group is a service holder given that the selected person is a male?
Solution :
Here, the condition is "The selected person is a male".
From, the given information, n(S) = 35.
Let A be the event of selecting a male person.
Then, n(A) = 20.
P(A) = n(A)/n(S)
= 20/35
= 4/7
Let B be the event of selecting a service holder.
Then, n(AnB) = 12.
P(AnB) = n(AnB)/n(S)
= 12/35
(Because, there are 12 male service holders)
The probability that a person selected at random from the group is a service holder given that the selected person is a male is
P(B/A) = P(AnB)/P(A)
= (12/35) / (20/35)
= (12/35) x (35/20)
= (12x35)/(35x20)
= 3/5
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 36)
Mar 02, 26 10:08 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 36) -
Doubling Time Growth Formula
Mar 02, 26 09:32 PM
Doubling Time Growth Formula - Formula - Problems with step by step solutions -
Half Life Decay Formula
Mar 02, 26 09:18 PM
Half Life Decay Formula - Concept - Problems with step by step explanation