COMPARING COEFFICIENT OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES AND SOLVING
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To compare the coefficients of linear equations in two variables, the equations must be in the form.
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
The following three cases are possible for any given system of linear equations.
(i) a1/a2 ≠ b1/b2, we get a unique solution
(ii) a1/a2 = a1/a2 = c1/c2, there are infinitely many solutions.
(iii) a1/a2 = a1/a2 ≠ c1/c2, there is no solution
Which of the following pairs of linear equations are consistent/inconsistent? if consistent, obtain the solution graphically.
Problems 1 :
x + y = 5 and 2 x + 2 y = 10
Solution :
x + y - 5 = 0
2 x + 2 y - 10 = 0
From the given equations, let us find the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 1, b1 = 1, c1 = -5
a2 = 2, b2 = 2, c2 = -10
a1/a2 = 1/2 -------(1)
b1/b2 = 1/2 -------(2)
c1/c2 = -5/(-10) = 1/2 -------(3)
This exactly matches the condition,
a1/a2 = b1/b2 = c1/c2
So, the system of equations will have infinitely many solution.
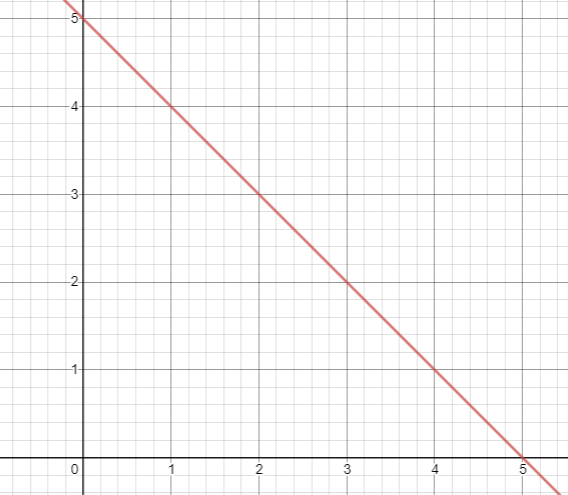
To draw the graph, let us find x and y intercepts.
x + y - 5 = 0
|
To find x - intercept : Put y = 0 x - 5 = 0 x = 5 (5, 0) |
To find y - intercept : Put x = 0 y - 5 = 0 y = 5 (0, 5) |
Both equations are representing the same line.
Problems 2 :
x - y = 8 and 3x - 3y = 16
Solution :
x - y – 8 = 0
3 x - 3 y -16 = 0
From the given equations, let us find the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 1, b1 = -1, c1 = -8
a2 = 3, b2 = -3, c2 = -16
a1/a2 = 1/3 -------(1)
b1/b2 = (-1)/(-3) = 1/3 -------(2)
c1/c2 = -8/(-16) = 1/2 -------(3)
This exactly matches the condition
a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
So, there is no solution.
Problems 3 :
2x + y - 6 = 0 and 4x - 2y - 4 = 0
Solution :
From the given equations, let us find the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 2, b1 = 1, c1 = -6
a2 = 4, b2 = -2, c2 = -4
a1/a2 = 2/4 = 1/2 -------(1)
b1/b2 = 1/(-2) = -1/2 -------(2)
c1/c2 = -6/(-4) = 3/2 -------(3)
This exactly matches the condition a1/a2 ≠ b1/b2
So, it has unique solution.
Graphing 1st equation,
2 x + y - 6 = 0
y = -2x + 6
|
x-intercept : Put y = 0 -2x + 6 = 0 -2x = -6 x = 3 (3, 0) |
y-intercept : Put x = 0 y = -2(0) + 6 y = 6 (0, 6) |
Graphing 2nd equation,
4 x - 2 y - 4 = 0
2y = 4x - 4
y = 2x - 2
|
x-intercept : Put y = 0 2x - 2 = 0 2x = 2 x = 1 (1, 0) |
y-intercept : Put x = 0 y = 2(0) - 2 y = -2 (0, -2) |
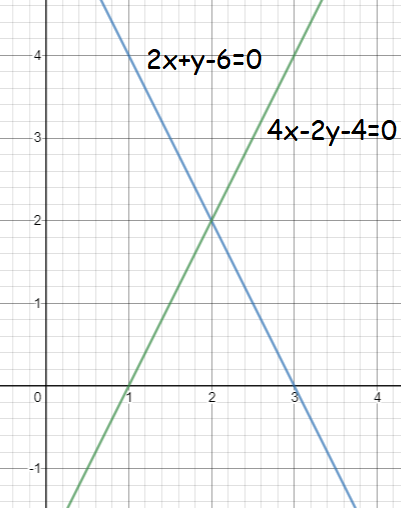
The above lines are intersecting at the point (2, 2). So, the solution is x = 2 and y = 2.
Problems 4 :
2x - 2y - 2 = 0
4x - 4y - 5 = 0
Solution :
From the given equations, let us find the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 2, b1 = -2, c1 = -2
a2 = 4, b2 = -4, c2 = -5
a1/a2 = 2/4 = 1/2 -------(1)
b1/b2 = -2/(-4) = 1/2 -------(2)
c1/c2 = -2/(-5) = 2/5 -------(3)
This exactly matches the condition a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
This exactly matches the condition
a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
So, there is no solution.
Problems 5 :
The pair of equations ax + 2y = 7 and 3x + by = 16 represent parallel lines if
(a) a = b (b) 3a = 2b (c) 2a = 3b (d) ab = 6
Solution :
ax + 2y = 7------(1)
3x + by = 16 ------(2)
Since the given lines are parallel, they must have same slope and different y-intercepts.
2y = -ax + 7
y = (-a/2)x + (7/2)
Slope = -a/2
by = -3x + 16
y = (-3/b) x + (16/b)
Slope = -3/b
-a/2 = -3/b
ab = 6
So, option d is correct.
Problems 6 :
Using the following equations:
(4/x) + 6y = 10 and (1/x) – 6y = 5
find the value of p if p = 3x.
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Solution :
(4/x) + 6y = 10 ------(1)
(1/x) – 6y = 5 ------(2)
Let a = 1/x, then
4a + 6y = 10 ------(1)
a – 6y = 5 ------(2)
Finding the value of a in terms of y,
a = 6y + 5
Applying the value of a, we get
4(6y + 5) + 6y = 10
24y + 20 + 6y = 10
30y = 10 - 20
30y = - 10
y = -10/30
y = -1/3
a = 6(-1/3) + 5
a = -2 + 5
a = 3
1/x = 3
x = 1/3
p = 3x ==> 3(1/3)
p = 1
Option a is correct.
Problems 7 :
The value of k for which the system of equations
x + y – 4 = 0 and 2x + ky = 3
has no solution, is
(a) – 2 (b) ≠ 2 (c) 3 (d) 2
Solution :
x + y – 4 = 0 and 2x + ky = 3
y = -x + 4 ----(1)
ky = -2x + 3
y = (-2/k) x + (3/k) ----(2)
Since the system has no solution, they must be parallel and they will never intersect.
Equating the slopes, we get
-1 = -2/k
k = 2
So, option d is correct.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Practice Problems Hard
Feb 17, 26 07:07 AM
SAT Math Practice Problems Hard -
Challenging SAT Math Problems
Feb 17, 26 06:45 AM
Challenging SAT Math Problems -
Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
Feb 17, 26 02:03 AM
Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers