CLASSIFYING TRIANGLES BY ANGLES WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
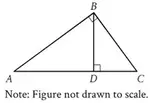
1. Identify the type of triangle whose diagram is given below.
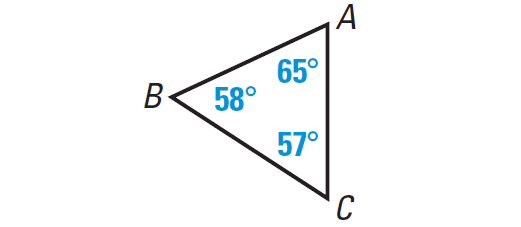
2. Identify the type of triangle whose diagram is given below.
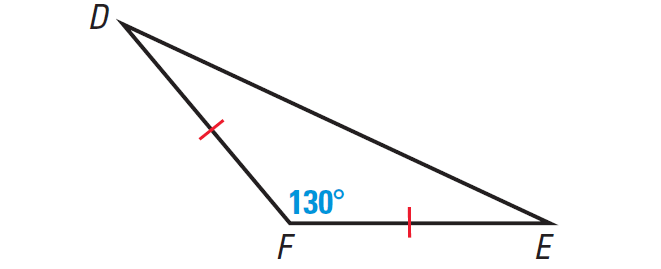
3. Identify the type of triangle whose diagram is given below.
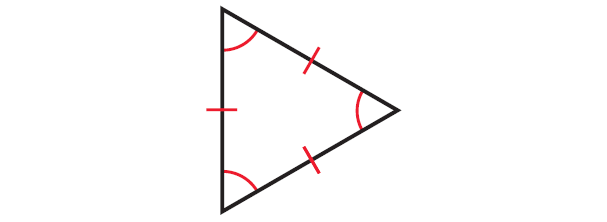
4. Identify the type of triangle whose diagram is given below.
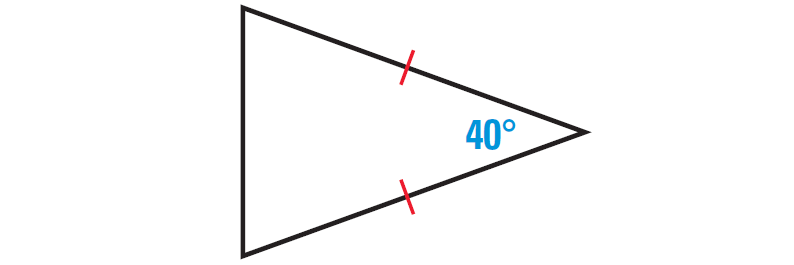
5. If (2x + 15)°, (3x)° and (6x)° are the angles of a triangle, identify the type of triangle.

1. Answer :

Let us consider the following two important points related to the given information.
(i) All the given three angles are different.
(ii) Each of the three angles is less than 90°
So, the given triangle is a scalene and acute triangle.
2. Answer :

Let us consider the following two important points related to the given information.
(i) One of the angles is greater than 90°
(ii) Two sides are equal in length. The angles formed by the two congruent sides with the third side also must be equal
So, the given triangle is an isosceles and obtuse triangle.
3. Answer :

In the triangle above, the lengths of all the three sides are same and all the three angles are congruent.
So, the given triangle is equiangular triangle.
4. Answer :

In the triangle above, two sides are congruent. The angles formed by the third side with two congruent sides will always be equal.
The diagram given below illustrates this.
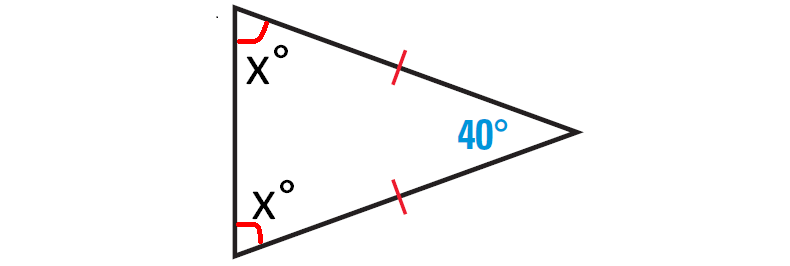
By Triangle Sum theorem,
x° + x° + 40° = 180°
2x + 40 = 180
Subtract 40 from both sides.
2x = 140
Divide both sides by 2.
x = 70
The angles measures of the given triangle are 40°, 70° and 70°.
Let us consider the following two important points from the above calculation.
(i) Two of the angles are equal
(ii) Each of the three angles is less than 90°
So, the given triangle is an isosceles and acute triangle.
5. Answer :
The angle sum property of a triangle states that the angles of a triangle always add up to 180°.
(2x + 15)° + (3x)° + (6x)° = 180°
2x + 15 + 3x + 6x = 180
Simplify.
11x + 15 = 180
Subtract 15 from each side.
11x = 165
Divide each side by 11.
x = 15
Substitute 15 for x into the given expressions to find the angles of the triangle.
First angle = 2x + 15 = 2(15) + 15 = 45°
Second angle = 3x = 3(15) = 45°
Third angle = 6x = 6(15) = 90°
Let us consider the following two important points from the above calculation.
(i) Two of the angles are equal
(ii) One of the angles is 90°
So, the given triangle is an isosceles and right triangle.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers -
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:35 AM
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)