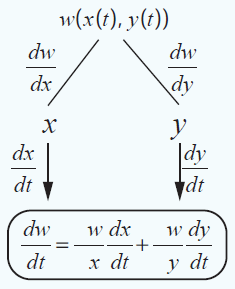
CHAIN RULE IN PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Suppose that W(x, y) is a function of two variables x, y having partial derivatives ∂W/∂x, ∂W/∂y. If both variables x, y are differentiable functions of a single variable t, then W is differentiable function t and
Problem 1 :
If
u(x, y) = x2y+3xy4, x = et and y = sin t
find du/dt and evaluate it at t = 0.
Solution :
du/dt = (∂u/∂x) (dx/dt) + (∂u/∂y) (dy/dt)
|
∂u/∂x = 2xy+3(1)y4 ∂u/∂x = 2xy+3y4 dx/dt = et |
∂u/∂y = x2(1)+3x(4y3) ∂u/∂y = x2+12xy3 dy/dt = cos t |
du/dt = (2xy+3y4)et + (x2+12xy3)cos t
du/dt = 2etxy+3ety4 + x2cos t+12xy3cos t
x = et and y = sin t
du/dt = 2etetsint+3etsin4t + (et)2cos t+12etsin3tcos t
du/dt = et(2etsint+3sin4t + etcos t+12sin3tcos t)
When t = 0
du/dt = e0(2e0sin(0)+3sin40 + etcos 0+12sin30cos 0)
du/dt = 1
Problem 2 :
If
u(x, y, z) = xy2z3, x = sint, y = cost, z = 1+e2t
find du/dt
Solution :
du/dt = (∂u/∂x) (dx/dt) + (∂u/∂y) (dy/dt) + (∂u/∂z) (dz/dt)
|
∂u/∂x = (1)y2z3 ∂u/∂x = y2z3 dx/dt = cost |
∂u/∂y = x(2y)z3 ∂u/∂y = 2xyz3 dy/dt = -sint |
∂u/∂z = xy2(3z2) ∂u/∂z = 3xy2z2 dz/dt = 0+e2t(2) dz/dt = 2e2t |
du/dt = y2z3cost + 2xyz3(-sint) + 3xy2z2(2e2t)
Applying x = sint t, y = cost and z = 1+e2t
du/dt = cos2t(1+e2t)3cost + 2sintcost (1+e2t)3(-sint) + 3sint cos2t (1+e2t)2(2e2t)
= (1+e2t)2[(1+e2t) cos3t - sin2tsint(1+e2t) + 6e2tsint cos2t]
Problem 3 :
If
w(x, y, z) = x2+y2+z2, x = et, y = et sint and z = etcost
find dw/dt.
Solution :
dw/dt = (∂w/∂x) (dx/dt) + (∂w/∂y) (dy/dt) + (∂w/∂z) (dz/dt) ----(1)
∂w/∂x = 2x
dx/dt = et
|
∂w/∂y = 2y dy/dt = et(cost)+sint(et) dy/dt = et[cost+sint] |
∂w/∂z = 2y dz/dt = et(-sint)+cost(et) dz/dt = et[cost-sint] |
By applying the values in (1), we get
= 2xet + 2yet[cost+sint] + 2zet[cost-sint]
= 2et[x+y(cost+sint)+z(cost-sint)]
= 2et[et+et sint(cost+sint)+etcost(cost-sint)]
= 2e2t[1+sintcost+sin2t+cos2t-sintcost]
= 2e2t(1+1)
= 4 e2t
Problem 4 :
Let
U(x, y, z) = xyz, x = e-t, y = e-tcost, z = sint, t ∈ℝ.
Find dU/dt.
Solution :
dU/dt = (∂U/∂x) (dx/dt) + (∂U/∂y) (dy/dt) + (∂U/∂z) (dz/dt) ----(1)
∂U/∂x = yz
dx/dt = -e-t
|
∂U/∂y = xz y = e-tcost dy/dt = e-t(-sint)+cost(-e-t) = e-t(-sint-cost) |
∂U/∂z = xy z = sint dz/dt = cost |
Applying the values in (1), we get
= yz(-e-t) + xze-t(-sint-cost) + xy (cost)
Applying the values of x = e-t, y = e-tcost, z = sint
Part 1 :
yz(-e-t) ==> e-tcost sint (-e-t) ==> -e-2tsint cost
Part 2 :
xze-t(-sint-cost) ==> e-tsinte-t(-sint-cost)
= e-2t sint(-sint-cost)
= e-2t sint(-sint-cost)
Part 3 :
xy (cost) = e-te-tcost (cost)
= e-2t cos2t
Adding part 1, 2 and 3, we get
= e-2t[-sint cost-sin2t-sint cost+cos2t]
= e-2t[cos2t-sin2t - 2sint cost]
= e-2t[cos2t - sin2t]

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 44)
Mar 05, 26 03:45 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 44) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 43)
Mar 04, 26 07:20 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 43) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 42)
Mar 04, 26 06:21 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 42)