AREA OF REGULAR POLYGON WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side length 4 inches.
Problem 2 :
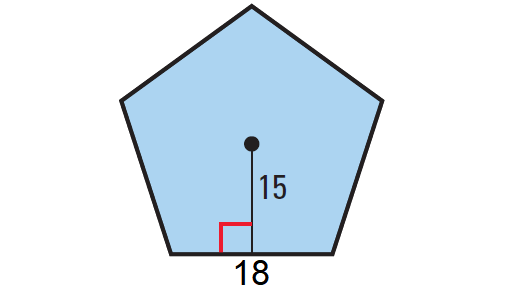
Find the area of the regular pentagon shown below.
Problem 3 :
A regular pentagon is inscribed in a circle with radius 1 unit. Find the area of the pentagon.
Problem 4 :
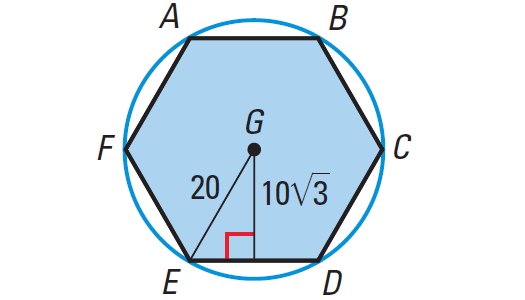
Find the area of the regular hexagon shown below.
Problem 5 :
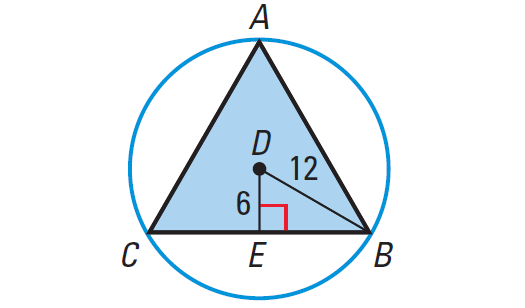
Find the area of the inscribed regular polygon shown below.
Problem 6 :
The enclosure on the floor underneath the Foucault Pendulum at the Houston Museum of Natural Sciences in Houston, Texas, is a regular dodecagon with a side length of about 4.3 feet and a radius of about 8.3 feet. What is the floor area of the enclosure ?

Answers
1. Answer :
The formula for area of an equilateral triangle is given by
A = √3/4 ⋅ s2
Plug s = 4
A = √3/4 ⋅ 42
Simplify.
A = √3/4 ⋅ 16
A = √3 ⋅ 4
A = 4√3
Hence, the area of the equilateral triangle is 4√3 square inches.
2. Answer :

To find area of any regular polygon, we need to know the length of apothem and perimeter.
In the above regular pentagon,
Apothem = 15 units
Pentagon has 5 sides. So, the perimeter is
P = side length ⋅ no. of sides
P = 18 ⋅ 5
P = 90 units
The formula for area of a n-gon is given by
A = 1/2 ⋅ apothem ⋅ perimeter of polygon
Substitute.
A = 1/2 ⋅ 15 ⋅ 90
Simplify.
A = 675
Hence, the area of the regular pentagon is 675 square units.
3. Answer :
Draw a sketch.
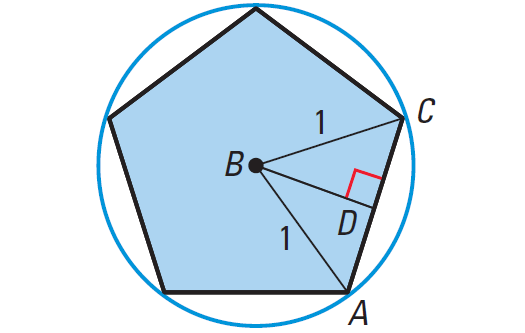
To apply formula for the area of a regular pentagon, we must find its apothem and perimeter.
The measure of central ∠ABC is
= 1/5 ⋅ 360°
= 72°
Let us consider the isosceles triangle ΔABC in the above regular pentagon.
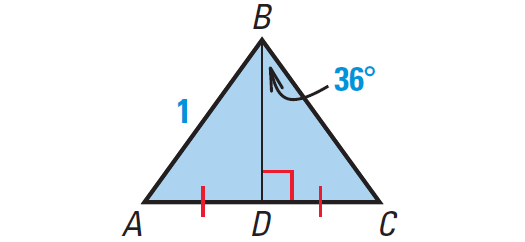
The altitude to base AC also bisects ∠ABC and side AC. The measure of ∠DBC, then, is 36°.
In right ΔDBC, we can use trigonometric ratios to find the lengths of the legs.
|
cos 36° = BD/BC cos 36° = BD/1 cos 36° = BD |
sin 36° = DC/BC sin 36° = DC/1 sin 36° = DC |
So, the pentagon has an apothem of
a = BD = cos 36°
and a perimeter of
P = 5(AC)
P = 5(2 ⋅ DC)
P = 10(DC)
P = 10 ⋅ sin 36°
The area of the pentagon is
A = 1/2 ⋅ apothem ⋅ perimeter of polygon
Substitute.
A = 1/2 ⋅ cos 36° ⋅ 10 ⋅ sin 36°
Simplify.
A = 5 ⋅ cos 36° ⋅ sin 36°
A ≈ 2.38 square units
4. Answer :

To apply formula for the area of a regular hexagon, we must be knowing the apothem and perimeter.
Apothem is already given and we have to find the side length (ED) of the polygon to find its perimeter.
Let us consider the isosceles triangle ΔGED in the above regular pentagon.
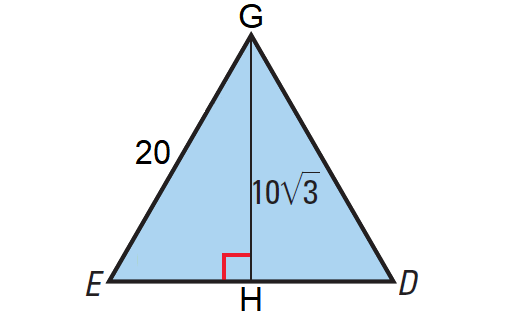
Because ΔGED is isosceles, the altitude GH to base ED bisects the side ED.
In right ΔEGH, we can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of EH.
EH2 + GH2 = EG2
Substitute.
EH2 + (10√3)2 = 202
EH2 + 300 = 400
Subtract 300 from each side.
EH2 = 100
Take square root on each side.
EH = 10
So, the hexagon has the perimeter of
P = 6(ED)
P = 6(2 ⋅ EH)
P = 6(2 ⋅ 10)
P = 6(20)
P = 120
The area of the hexagon is
A = 1/2 ⋅ apothem ⋅ perimeter of polygon
Substitute.
A = 1/2 ⋅ 10√3 ⋅ 120
Simplify.
A = 600√3 square units
5. Answer :

To apply formula for the area of a regular polygon, we must be knowing the apothem and perimeter.
Apothem is already given and we have to find the side length (CB) of the triangle to find its perimeter.
Because ΔABC is equilateral (Regular Polygon), DE bisects the side CB.
In right ΔDEB, we can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of EB.
EB2 + DE2 = DB2
Substitute.
EB2 + 62 = 122
EB2 + 36 = 144
Subtract 36 from each side.
EB2 = 108
Take square root on each side.
√EB2 = √108
Simplify.
EB = 6√3
So, the triangle has the perimeter of
P = 3(CB)
P = 3(2 ⋅ EB)
P = 3(2 ⋅ 6√3)
P = 36√3
The area of the triangle is
A = 1/2 ⋅ apothem ⋅ perimeter of polygon
Substitute.
A = 1/2 ⋅ 6 ⋅ 36√3
Simplify.
A = 108√3 square units
6. Answer :
Draw a sketch.
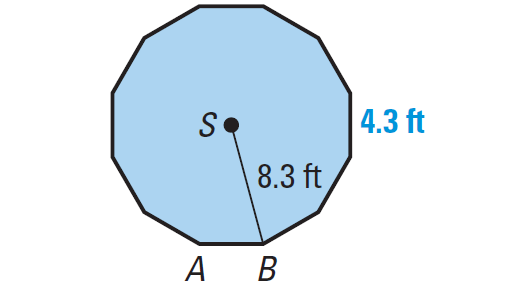
To apply formula for the area of a regular polygon, we must find its apothem and perimeter.
A dodecagon has 12 sides. So, the perimeter of the enclosure is
P ≈ 12(4.3)
P ≈ 51.6 feet
Let us consider the isosceles triangle ΔSAB in the above regular dodecagon.
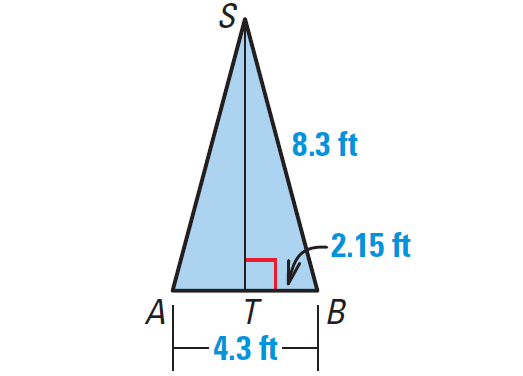
In right ΔSBT, we have
BT = 1/2 ⋅ BA
BT = 1/2 ⋅ (4.3)
BT = 2.15
In right ΔSBT, we can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the apothem ST.
ST2 + BT2 = BS2
ST2 + (2.15)2 = 8.32
ST2 + (2.15)2 = 8.32
ST2 + 4.6225 = 68.89
Subtract 4.6225 from each side.
ST2 = 64.2675
Take square root on each side.
ST ≈ 8 feet
So, the floor area of the enclosure is
A = 1/2 ⋅ apothem ⋅ perimeter of polygon
A ≈ 1/2 ⋅ 8 ⋅ 51.6
A ≈ 206.4 square feet
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 4)
Feb 20, 26 05:55 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 4) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 3)
Feb 20, 26 05:37 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 3) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 2)
Feb 19, 26 07:14 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 2)