AREA BETWEEN TWO CURVES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
General Area Principle
Let f and g be two continuous curves, with f lying above g as shown below.
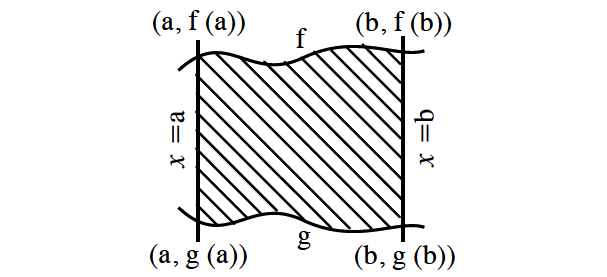
Then the area R between f and g, from x = a to x = b, is given by
No restriction on f and g where they lie. Both may be lie above or below the x-axis or g lies below and f lies above the x-axis.
Example 1 :
Find the area between the line and curve whose equations are given below.
y = x + 1
y = x2 - 1
Solution :
To get the points of intersection of the line and curve, we have to solve the equations y = x + 1 and y = x2 - 1.
y = y
x2 - 1 = x + 1
x2 - 1 - x - 1 = 0
x2 - x - 2 = 0
x2 + x - 2x - 2 = 0
x(x + 1) - 2(x + 1) = 0
(x + 1)(x - 2) = 0
x + 1 = 0 or x - 2 = 0
x = -1 or x = 2
The line intersects the curve at x = -1 and x = 2.
y = x2 - 1 is a parabola which opens up.
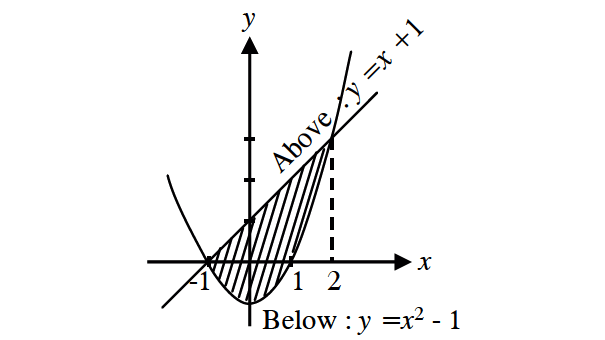
Required Area :
Example 2 :
Find the area bounded by the curve and line whose equatoion are given below.
y = x3
y = x
Solution :
To get the points of intersection, solve the given equations.
y = y
x3 = x
x3 - x = 0
x(x2 - 1) = 0
|
x = 0 |
x2 - 1 = 0 x2 - 12 = 0 (x + 1)(x - 1) = 0 x = -1 or x = 1 |
The line intersects the curve at x = 0, x = -1 and x = 1.
The line y = x lies above the curve y = x3 in the first quadrant and y = x3 lies above the line y = x in the third quadrant.
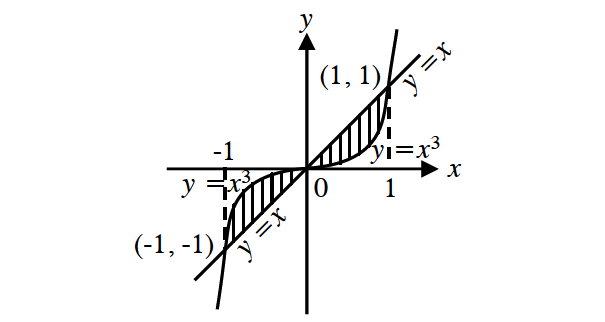
Required Area :
Example 3 :
Find the area of the region enclosed by the curve and the line whose equations are given bvelow.
y2 = x
y = x - 2
Solution :
y2 = x ----(1)
y = x - 2 ----(2)
Solve (2) for x.
x = y + 2 ----(3)
Find the points of intersection by solving (1) and (3).
x = x
y2 = y + 2
y2 - y - 2 = 0
y2 + y - 2y - 2 = 0
y(y + 1) - 2(y + 1) = 0
(y + 1)(y - 2) = 0
y + 1 = 0 or y - 2 = 0
y = -1 or y = 2
The line intersects the curve at y = -1 and y = 2.
y2 = x is a parabola which opens to the right.
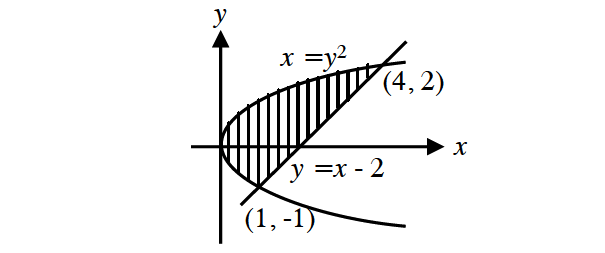
To compute the region shown above by integrating with respect to x, we would have to split the region into two parts, because the equation of the lower boundary changes at x = 1.
However if we integrate with respect to y, splitting is not necessary.
Required Area :
Example 4 :
Find the area of the region common to the circle and parabola whose equations are given below.
x2 + y2 = 16
y2 = 6x
Solution :
The points of intersection of the given circle and parabola are
(2, 2√3) and (2, -2√3)
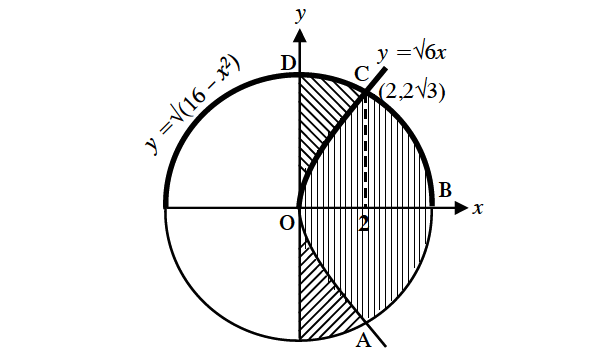
Required area is OABC.
Due to symmetrical property, the required area OABC is equal to 2 times the area of OBC.
That is, 2[(area bounded by y2 = 6x, x = 0, x = 2 and x-axis) + (area bounded by x2 + y2 = 16, x = 2, x = 4 and x-axis)}
Solve the given equations of circle and parabola for y.
|
|
|
Required Area :
Example 5 :
Compute the area between the curve y = sin x and y = cosx and the lines x = 0 and x = π.
Solution :
To find the points of intersection solve the two equations.
y = y
sinx = cosx
From x = 0 and x = π, we have
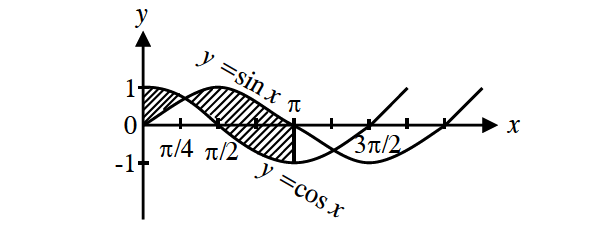
From the figure we see that cos x > sin x for
and sin x > cos x for
Required Area :
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22)
Feb 26, 26 08:43 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22) -
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers
Feb 25, 26 08:07 AM
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers -
Solving Exponential Equations
Feb 23, 26 10:06 AM
Solving Exponential Equations - Concept - Examples