ARC AND ANGLE RELATIONSHIPS IN CIRCLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
When chords, secants, and tangents intersect in a circle (Figure 1), on a circle (Figure 2), or outside of a circle (Figure 3), special relationships exist between the angle and arc measures formed.
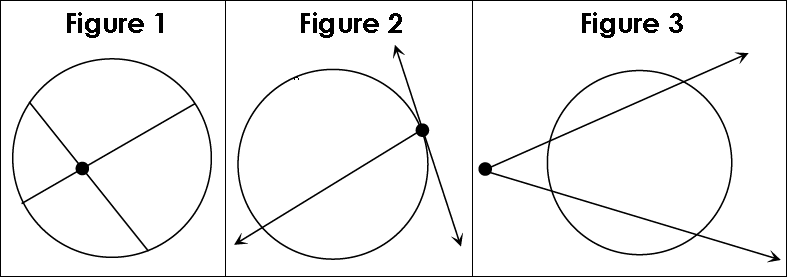
Interior Intersections
If two secants or chords intersect inside a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is equal to half the sum of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
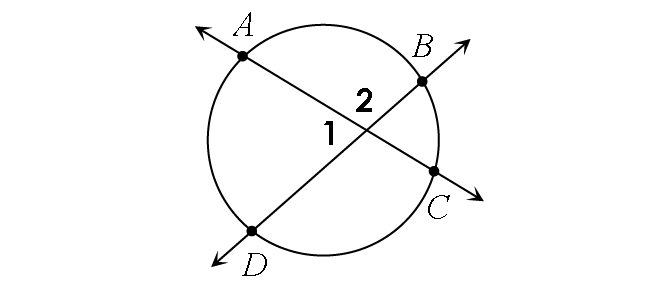
In the diagram above,
m∠1 = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc AD + m∠arc BC)
m∠2 = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc AB + m∠arc CD)
Example 1 :
Find m∠AED.
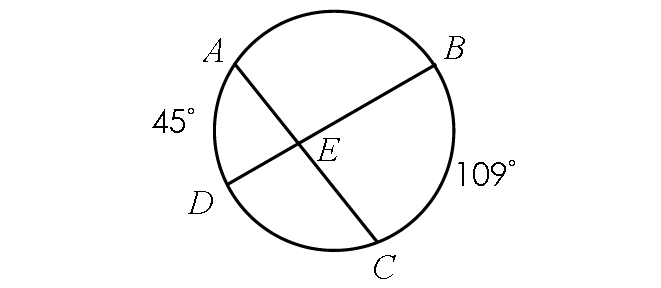
Solution :
m∠AED = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc AD + m∠arc BC)
Substitute.
m∠AED = ½ ⋅ (45° + 109°)
m∠AED = ½ ⋅ 154°
m∠AED = 77°
Example 2 :
Find m∠YWX.
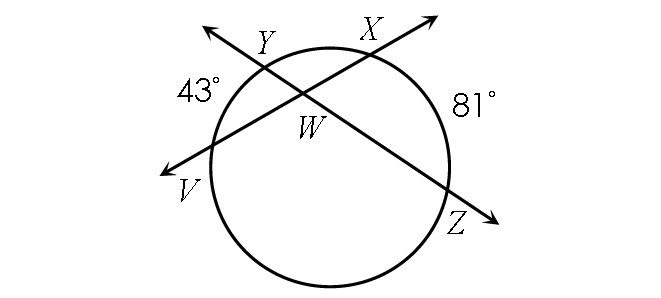
Solution :
Find m∠VWY :
m∠VWY = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc VY + m∠arc XZ)
m∠VWY = ½ ⋅ (43° + 81°)
m∠VWY = ½ ⋅ 124°
m∠VWY = 62°
Find m∠YWX :
m∠VWY and m∠YWX are linear pair.
Then,
m∠VWY + m∠YWX = 180°
Substitute m∠VWY = 62°.
62° + m∠YWX = 180°
Subtract 62° from each side.
m∠YWX = 118°
Example 3 :
Find m∠arc CDE.
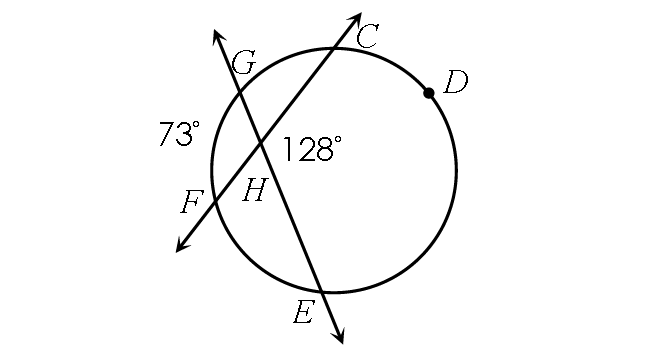
Solution :
½ ⋅ (m∠arc GF + m∠arc CDE) = m∠CHE
Substitute.
½ ⋅ (73° + m∠arc CDE) = 128°
Multiply each side by 2.
73° + m∠arc CDE = 256°
Subtract 73° from each side.
m∠arc CDE = 183°
Video Lesson 1
Video Lesson 2
On the Circle Intersections
If a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of tangency, then the measure of each angle formed is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
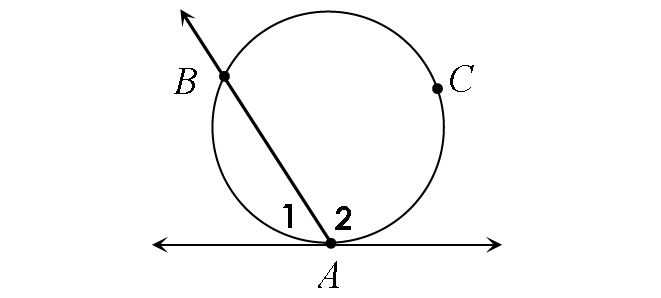
In the diagram above,
m∠1 = ½ ⋅ m∠arc AB
m∠2 = ½ ⋅ m∠arc ACB
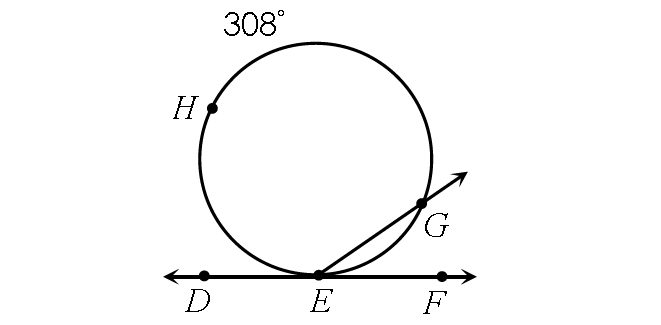
Example 4 :
Find m∠DEG.
Solution :
m∠DEG = ½ ⋅ m∠arc EHG
Substitute.
m∠DEG = ½ ⋅ 308°
m∠DEG = 154°
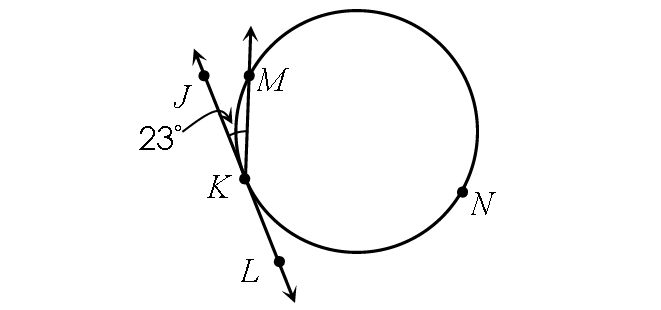
Example 5 :
Find m∠arc KNM.
Solution :
Find m∠arc KM :
½ ⋅ m∠arc KM = m∠JKM
Substitute.
½ ⋅ m∠arc KM = 23°
Multiply each side by 2.
m∠arc KM = 46°
In the circle above,
m∠arc KM + m∠arc KNM = 360°
Substitute.
46° + m∠arc KNM = 360°
Subtract 46° from each side.
m∠arc KNM = 314°
Exterior Intersections
If secants and/or tangents intersect on the exterior of a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is equal to half the difference of the intercepted arcs.
Two Secants
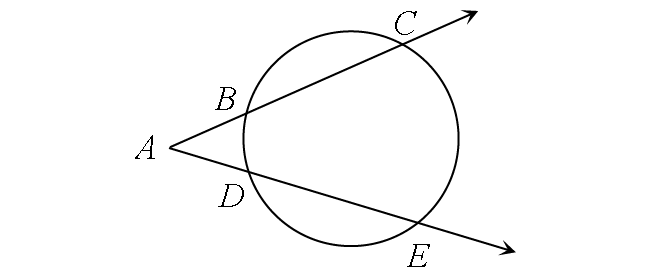
m∠A = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc CE - m∠arc BD)
Secant and Tangent
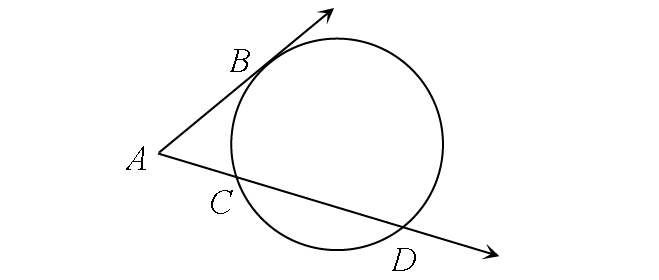
m∠A = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc BD - m∠arc BC)
Two Tangents
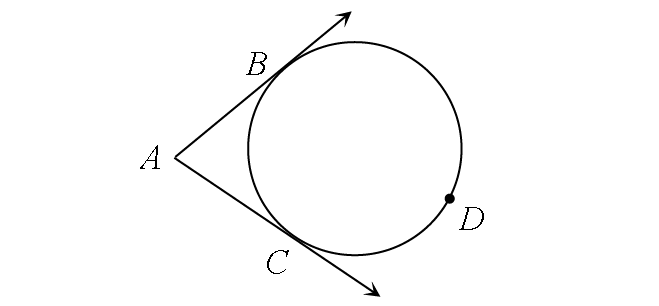
m∠A = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc BDC - m∠arc BC)
Example 6 :
Find m∠KLM.
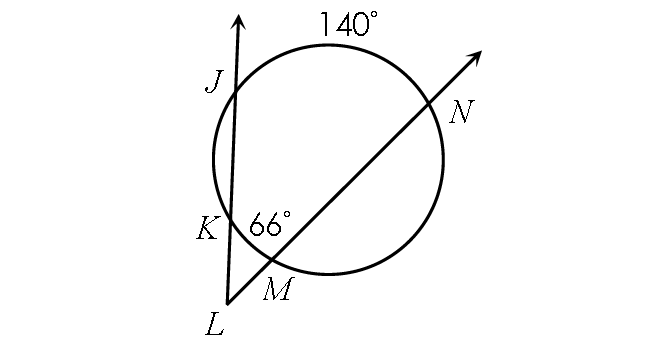
Solution :
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc JN - m∠arc KM)
Substitute.
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ (140° - 66°)
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ 74°
m∠KLM = 37°
Example 7 :
Find m∠BCD.
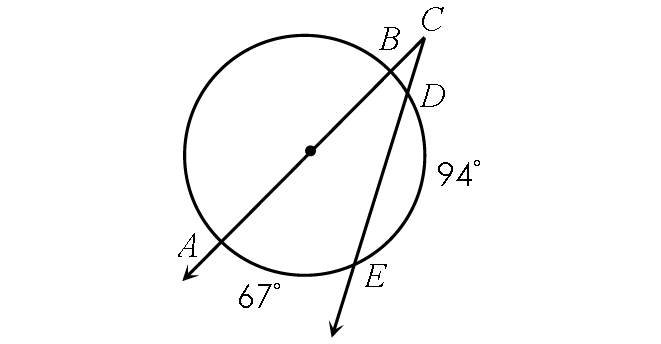
Solution :
In the circle above,
m∠arc BD + m∠arc DE + m∠arc EA = 180°
Substitute.
m∠arc BD + 94° + 67° = 180°
m∠arc BD + 161° = 180°
Subtract 161° from each side.
m∠arc BD = 19°
Finding m∠BCD :
m∠BCD = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc AE - m∠arc BD)
Substitute.
m∠BCD = ½ ⋅ (67° - 19°)
m∠BCD = ½ ⋅ 48°
m∠BCD = 24°
Example 8 :
Find m∠KLM.
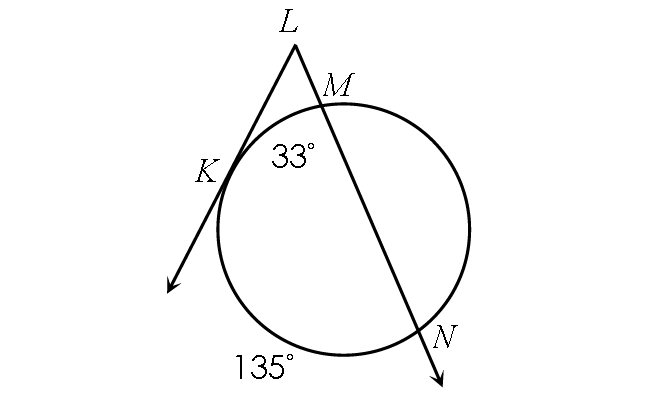
Solution :
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc KN - m∠arc KM)
Substitute.
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ (135° - 33°)
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ 102°
m∠KLM = 51°
Example 9 :
Find m∠CDE.
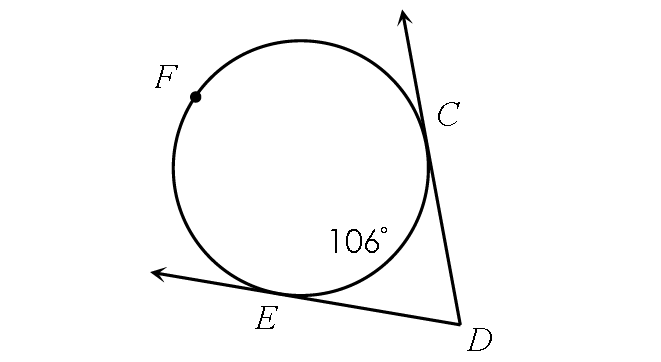
Solution :
In the circle above,
m∠arc CFE + m∠arc CE = 360°
Substitute.
m∠arc CFE + 106° = 360°
Substitute 106° from each side.
m∠arc CFE = 254°
Finding m∠CDE :
m∠CDE = ½ ⋅ (m∠arc CFE - m∠arc CE)
Substitute.
m∠CDE = ½ ⋅ (254° - 106°)
m∠KLM = ½ ⋅ 148°
m∠KLM = 74°
Example 10 :
Find m∠arc MK.
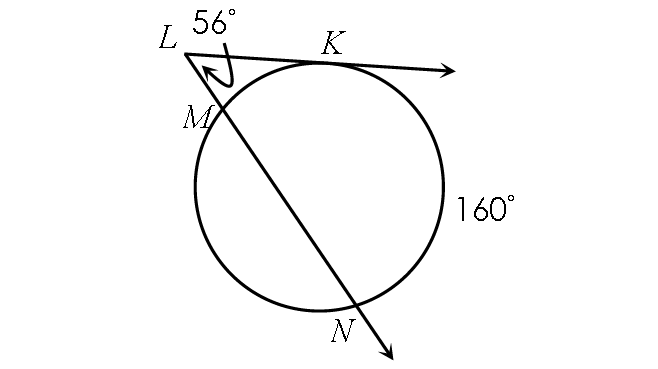
½ ⋅ (m∠arc NK - m∠arc MK) = m∠MLK
Substitute.
½ ⋅ (160° - m∠arc MK) = 56°
Multiply each side by 2.
160° - m∠arc MK = 112°
Subtract 160° from each side.
- m∠arc MK = -48°
Multiply each side by -1.
m∠arc MK = 48°
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)