ANGLES AND THEIR MEASUREMENT
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
An angle consists of two different rays that have the same initial point. The rays are the sides of the angles. The initial point is the vertex of the angle.
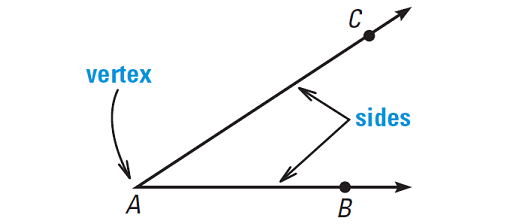
The angle that has sides AB and AC is denoted by ∠BAC, ∠CAB or ∠A. The point A is the vertex of the angle.
In this section, we are going to study two postulates about the measures of angles.
Postulate 1 (Protractor Postulate)
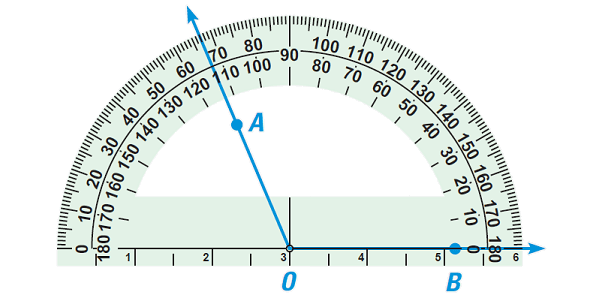
Consider a point A on one side of OB. The rays of the form OA can be matched one to one with the real numbers from 0 to 180.
The measure of ∠AOB is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the real numbers for OA and OB.
Postulate 2 (Angle Addition Postulate)
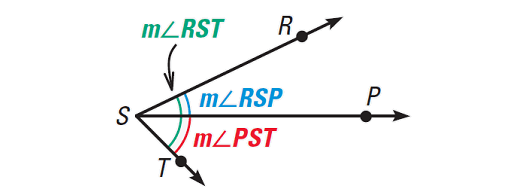
If P is in the interior of ∠RST, then we have
m∠RSP + m∠PST = m∠RST
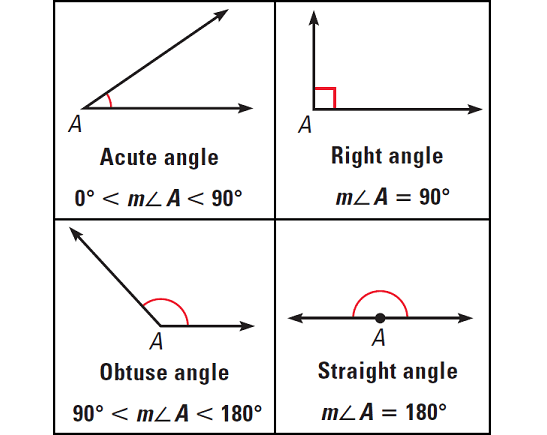
Classifying Angles
Angles are classified as acute, right, obtuse and straight, according to their measures. Angles have measures greater than 0°.
Example 1 :
Name the angles in the figure given below.
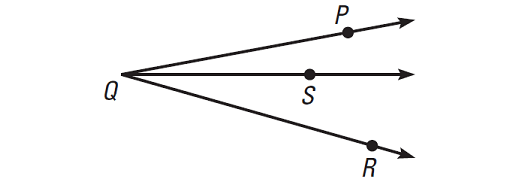
Solution :
There are three different angles.
∠PQS or ∠SQP
∠SQR or ∠RQS
∠PQR or ∠RQP
We should name any of the angles as ∠Q, because all three angles have Q as their vertex. The name ∠Q would not distinguish one angle from others.
Example 2 :

Each eye of a horse wearing blinkers has an angle of vision that measures 100°. The angle of vision that is seen by both eyes measures 60°.
Find the angle of vision seen by the left eye alone.
Solution :
We can use the angle addition postulate.
m∠2 + m∠3 = 100° (The total for left eye is 100°)
m∠3 = 100° - m∠2 (Subtract m∠2 from each side)
m∠3 = 100° - 60° (Substitute 60° for m∠2)
m∠3 = 40° (Subtract)
Hence, the vision for the left eye alone measures is 40°.
Example 3 :
Plot the points L (-4, 2), M(-1, -1), N (2, 2), Q(4, -1) and P(2, -4). Then, measure and classify the following angles as acute, right, obtuse or straight.
(i) m∠LMN
(ii) m∠LMP
(iii) m∠NMQ
(iv) m∠LMQ
Solution :
Plot the given points in xy coordinate plane.

We can use the protractor to measure and classify each angle as shown below.
|
Measure (i) m∠LMN = 90° (ii) m∠LMP = 180° (iii) m∠NMQ = 45° (iv) m∠LMQ = 135° |
Classification Right angle Straight angle Acute angle Obtuse angle |
Note :
Two angles are adjacent angles, if they share a common vertex and side, but have no common interior points.
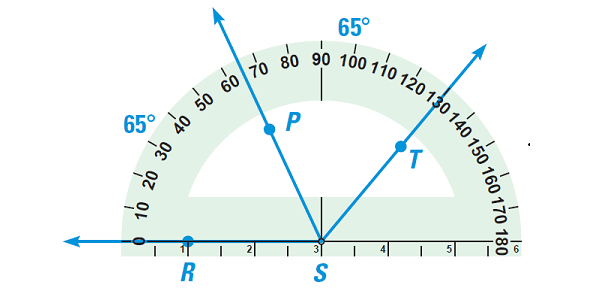
Example 4 :
Use a protractor to draw two adjacent acute angles ∠RSP and ∠PST so that ∠RST is
(a) Acute
(b) Obtuse
Solution :
Solution (a) :
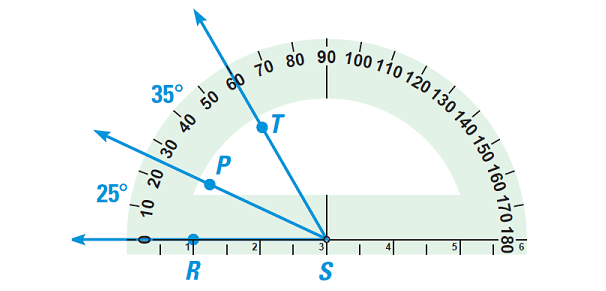
Solution (b) :
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers -
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:35 AM
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)