ALGEBRAIC REPRESENTATIONS OF TRANSFORMATIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To translate or reflect or rotate a figure in the coordinate plane, we have to transform each of its vertices. Then, we have to connect the vertices to form the image.
We can use the rules shown in the tables which describe how coordinates change for different types of transformations.
Rules for Translation
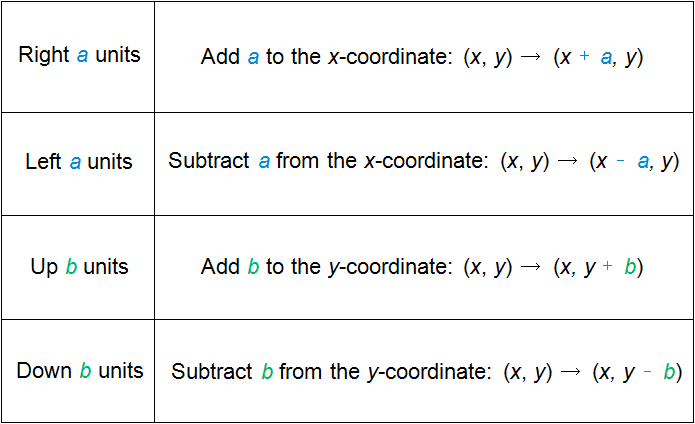
Rules for Reflection
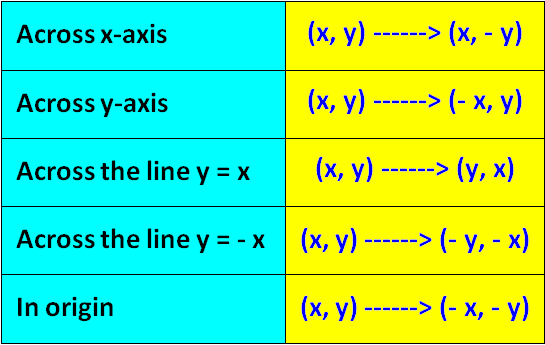
Rules for Rotation
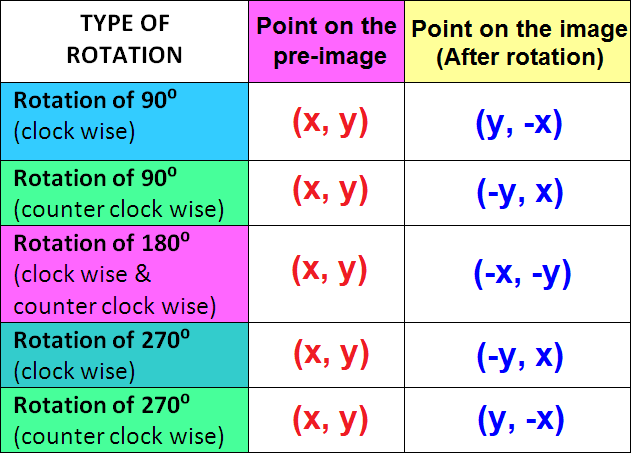
Example 1 :
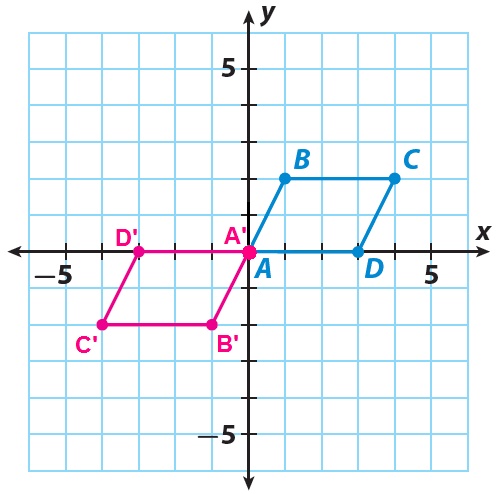
Trapezoid ABCD has the vertices A (1, 0), B(4, 0), C(4, -4) and D(0, -4). Graph the trapezoid ABCD and its image after a translation of 5 units to the left and 3 units up.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Let A', B', C' and D' be the vertices of the translated figure.
Since there is a translation of 5 units to the left and 3 units up, we have to subtract 5 from x-coordinate and add 3 to y-coordinate of each vertex.
A' ------> (1-5, 0+3) = (-4, 3)
B' ------> (4-5, 0+3) = (-1, 3)
C' ------> (4-5, -4+3) = (-1, -1)
D' ------> (0-5, -4+3) = (-5, -1)
Step 2 :
Sketch the trapezoid ABCD and its image A'B'C'D'.
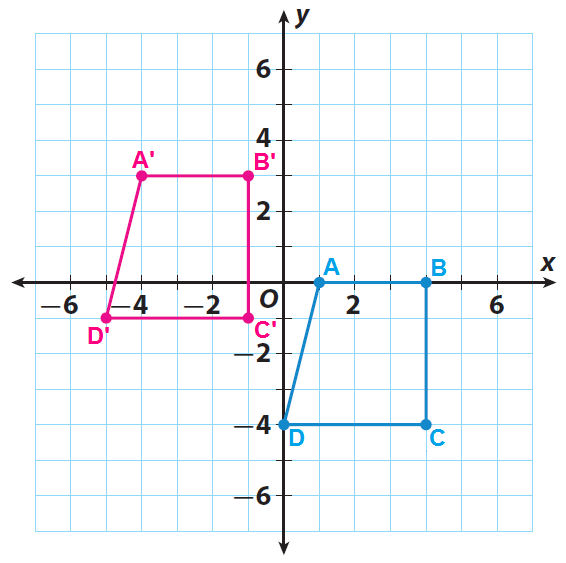
Example 2 :
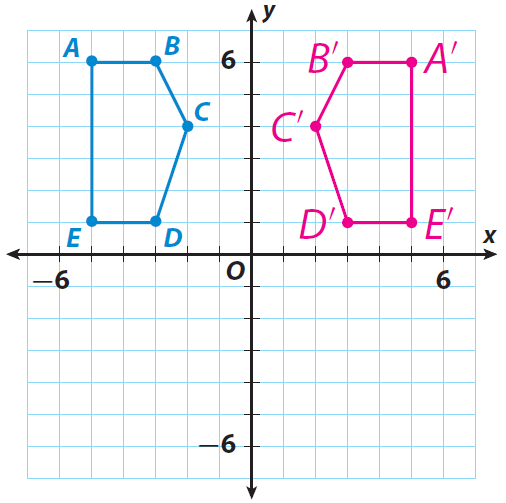
A pentagon has the vertices A(-5, 6), B(-3, 6), C(-2, 4), D(-3, 1) and E(-5,1). Find the vertices of rectangle A'B'C'D'E' after a reflection across the y-axis. Then graph the pentagon and its image.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Apply the rule to find the vertices of the image.
Since there is a reflection across the y-axis, we have to multiply each x-coordinate by -1.
That is, (x, y) ----> (-x, y).
Step 2 :
A(-5, 6) ----> A'(5, 6)
B(-3, 6) ----> B'(3, 6)
C(-2, 4) ----> C'(2, 4)
D(-3, 1) ----> D'(3, 1)
E(-5, 1) ----> E'(5, 1)
Step 3 :
Graph the pentagon ABCDE and its image.
Example 3 :
The triangle XYZ has the following vertices X(0, 0), Y(2, 0) and Z(2, 4). Rotate the triangle XYZ 90° counterclockwise about the origin.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Trace triangle XYZ and the x- and y-axes onto a piece of paper.
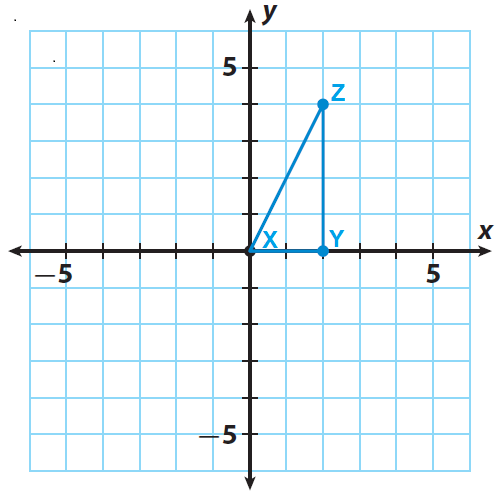
Step 2 :
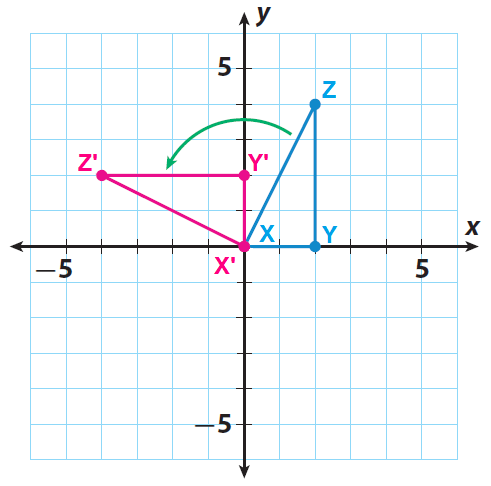
Let X', Y' and Z' be the vertices of the rotated figure.
Since the triangle is rotated 90° counterclockwise about the origin, the rule is
(x, y) ------> (-y, x)
Step 3 :
X(0, 0) ------> X'(0, 0)
Y(2, 0) ------> Y'(0, 2)
Z(2, 4) ------> Z'(-4, 2)
Step 4 :
Sketch the image X'Y'Z' using the points X'(0, 0), Y'(0, 2) and Z'(-4, 2).
Example 4 :
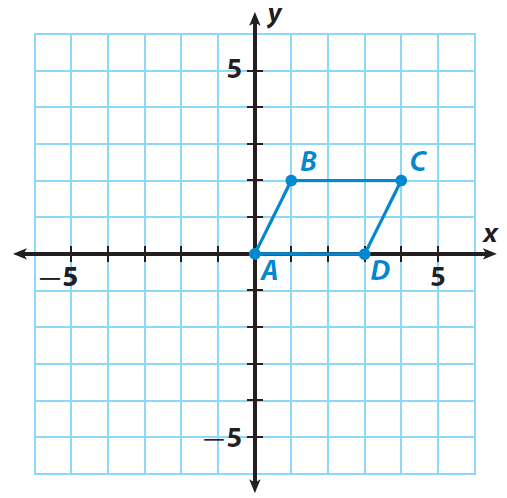
A quadrilateral has the following vertices A(0, 0), B(1, 2), C(4, 2) and D(3, 0). Rotate the quadrilateral 180° clockwise about the origin.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Trace the quadrilateral ABCD and the x- and y-axes onto a piece of paper.
Step 2 :
Let A', B', C' and D' be the vertices of the rotated figure.
Since the quadrilateral is rotated 180° clockwise about the origin, the rule is
(x, y) ------> (-x, -y)
Step 3 :
A(0, 0) ------> A'(0, 0)
B(1, 2) ------> B'(-1, -2)
C(4, 2) ------> C'(-4, -2)
D(3, 0) ------> D'(-3, 0)
Step 4 :
Sketch the image A'B'C'D' using the points A'(0, 0), B'(-1, -2), C(-4, -2) and D'(-3, 0).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


