ALGEBRA AND ANGLE MEASURES WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
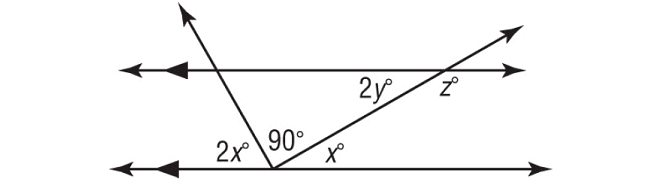
Problem 1 :
Find the values of x, y and z.
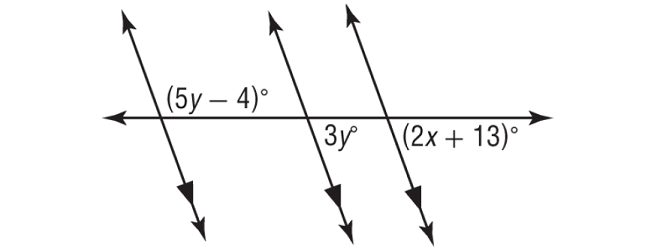
Problem 2 :
Find the values of x and y.
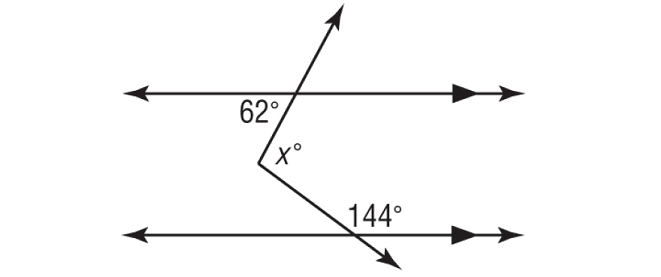
Problem 3 :
Using a 3rd parallel Line – Auxiliary Line, find the value of x.
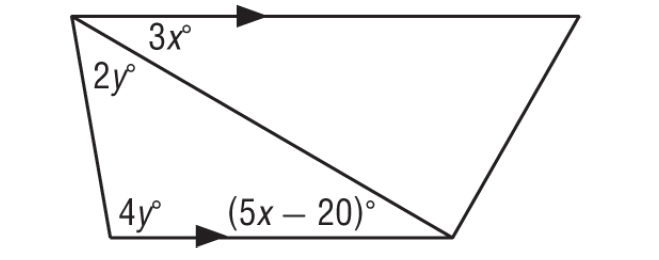
Problem 4 :
Find the values of x and y.
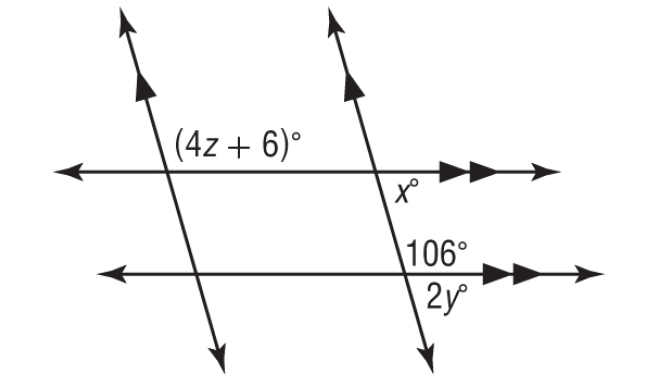
Problem 5 :
Find the values of x, y and z.
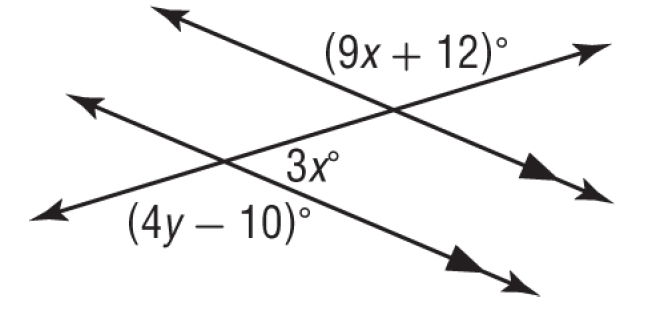
Problem 6 :
Find the values of x and y.
Problem 7 :
Solve for x.
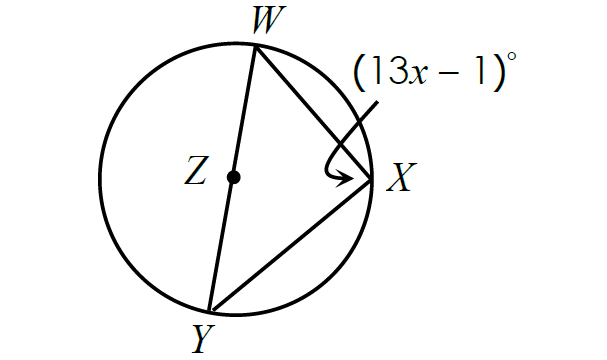
Problem 8 :
Solve for x.
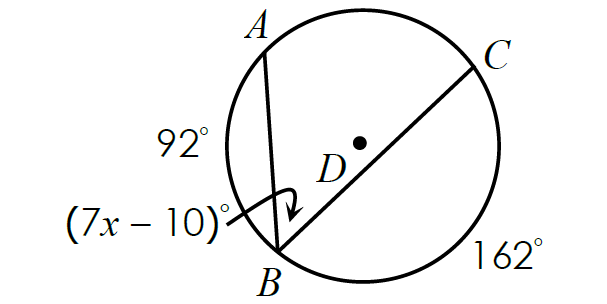
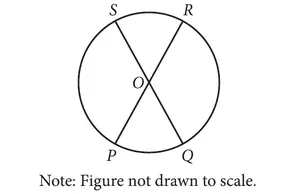
Problem 9 :
If m∠ABD = (6x + 26)° and m∠ACD = (13x – 9)°, find the value of x.
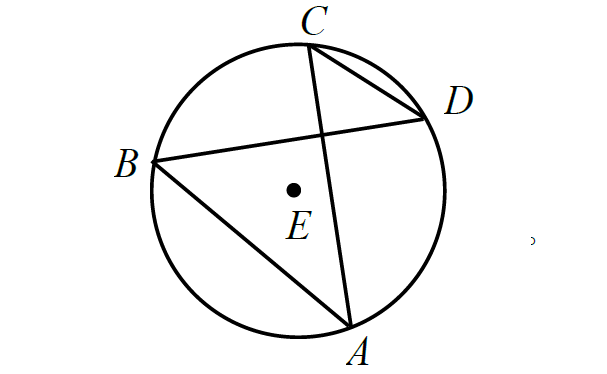
Problem 10 :
Solve for x.
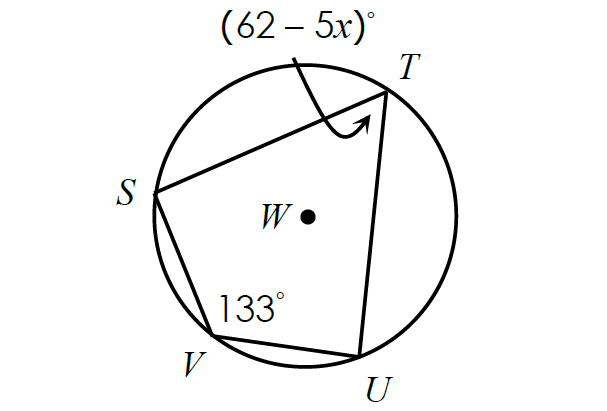

1. Answer :
2x°, 90° and x° together form a straight angle.
2x° + 90° + x° = 180°
3x + 90 = 180
Subtract 90 from each side.
3x = 90
Divide each side by 3.
x = 30
x° and 2y° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
2y° = x°
2y = x
Substitute x = 30.
2y = 30
Divide each side by 2.
y = 15
Therefore,
x = 30 and y = 15
2. Answer :
Mark a new angle a°.
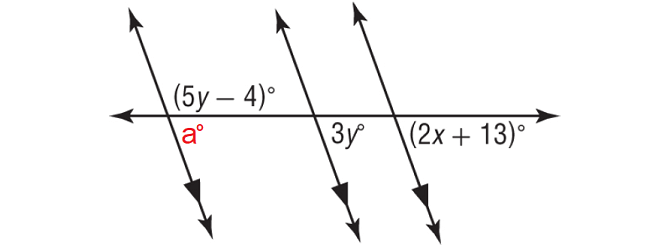
a° and (5y - 4)° form a linear pair.
a° + (5y - 4)° = 180°
a° and 3y° are corresponding angles, then a° = 3y°.
3y° + (5y - 4)° = 180°
3y + 5y - 4 = 180
8y - 4 = 180
Add 4 to each side.
8y = 184
Divide each side by 8.
y = 23
3y° and (2x + 13)° are corresponding angles and they are equal.
(2x + 13)° = 3y°
2x + 13 = 3y
Substitute y = 23.
2x + 13 = 3(23)
2x + 13 = 69
Subtract 13 from each side.
2x = 56
Divide each side by 2.
x = 28
3. Answer :
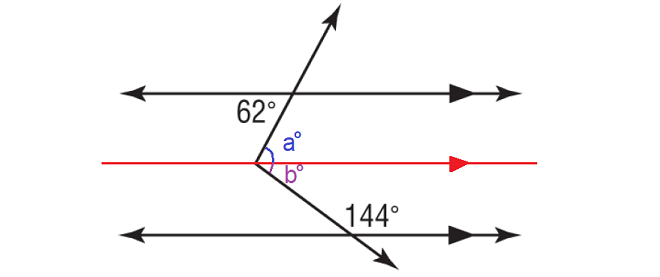
In the figure above, a° and 62° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
a° = 62°
b° and 144° are interior angles on the same side of the transversal and they are supplementary.
b° + 144° = 180°
Subtract 144° from each side.
b° = 36°
In the above figure,
x = a + b
= 62 + 36
= 98
4. Answer :
3x° and (5x - 20)° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
3x° = (5x - 20)°
3x = 5x - 20
Subtract 3x from each side.
0 = 2x - 20
Add 20 to each side.
20 = 2x
Divide each side by 2.
10 = x
By Triangle Angle Sum Theorem,
(5x - 20)° + 2y° + 4y° = 180°
5x - 20 + 2y + 4y = 180
5x - 20 + 6y = 180
Substitute x = 10.
5(10) - 20 + 6y = 180
50 - 20 + 6y = 180
30 + 6y = 180
Subtract 30 from each side.
6y = 150
Divide each side by 6.
y = 25
Therefore,
x = 10 and y = 25
5. Answer :
2y° and 106° form a linear pair, they are supplementary.
2y° + 106° = 180°
2y + 106 = 180
Subtract 106 from each side.
2y = 74
Divide each side by 2.
y = 37
x° and 2y° are corresponding angles, they are equal.
x° = 2y°
x = 2y
Substitute x = 37.
x = 2(37)
x = 74
Using Vertical angles Theorem, mark the angle x°.
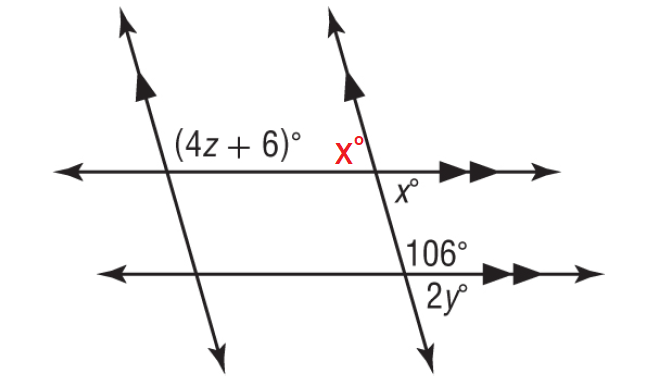
In the figure above, (4z + 6)° and x° are consecutive interior angles, they are supplementary.
(4z + 6)° + x° = 180°
4z + 6 + x = 180
Substitute x = 74.
4z + 6 + 74 = 180
4z + 80 = 180
Subtract 80 from each side.
4z = 100
Divide each side by 4.
z = 25
Therefore,
x = 74, y = 37 and z = 25
6. Answer :
Mark a new angle a°.
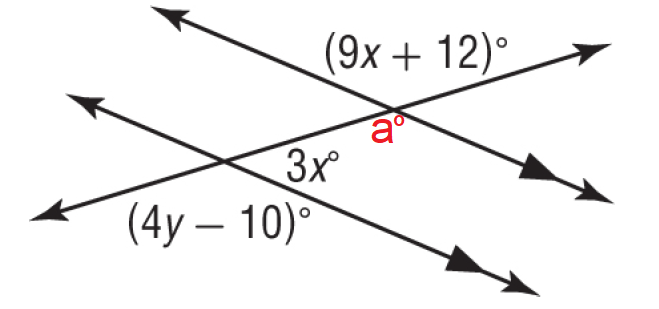
(9x + 12)° and a° are consecutive interior angles, they are supplementary.
a° + 3x° = 180°
By Vertical Angles Theorem, a° = (9x + 12)°.
(9x + 12)° + 3x° = 180°
9x + 12 + 3x = 180
12x + 12 = 180
Subtract 12 from each side.
12x = 168
Divide each side by 12.
x = 14
(4y - 10)° and 3x° form a linear pair, they are supplementary.
(4y - 10)° + 3x° = 180°
4y - 10 + 3x = 180
Substitute x = 14.
4y - 10 + 3(14) = 180
4y - 10 + 42 = 180
4y + 32 = 180
Subtract 32 from each side.
4y = 148
Divide each side by 4.
y = 37
Therefore,
x = 14 and y = 37
7. Answer :
Since the inscribed angle ∠WXY intercepts the diameter, it is a right angle.
m∠WXY = 90°
(13x - 1)° = 90°
13x - 1 = 90
Add 1 to each side.
13x = 91
Divide each side by 13.
x = 7
8. Answer :
In the figure above,
m∠arc AC + 162° + 92° = 360°
m∠arc AC + 254° = 360°
Subtract 254° from each side.
m∠arc AC = 106°
The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half of the measure of its intercepted arc.
m∠ABC = (1/2) ⋅ m∠arc AC
(7x - 10)° = (1/2) ⋅ 106°
(7x - 10)° = 53°
7x - 10 = 53
Add 10 to each side.
7x = 63
Divide each side by 7.
x = 9
9. Answer :
In the figure above, two inscribed angles ∠ABD and ∠ACD intercept the same arc AD. Then, ∠ABD and ∠ACD are congruent.
m∠ABD = m∠ACD
(6x + 26)° = (13x - 9)°
6x + 26 = 13x - 9
Subtract 6x from each side.
26 = 7x - 9
Add 9 to each side.
35 = 7x
Divide each side by 7.
5 = x
10. Answer :
Since the quadrilateral STUV is inscribed in a circle, its opposite angles are supplementary.
m∠T + m∠V = 180°
Substitute.
(62 - 5x)° + 133° = 180°
62 - 5x + 133 = 180
195 - 5x = 180
Subtract 195 from each side.
-5x = -15
Divide each side by -5.
x = 3
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 46)
Jan 27, 26 07:05 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 46) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 45)
Jan 19, 26 06:14 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 45) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)
Jan 12, 26 06:35 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)