ADD AND SUBTRACT RADICAL EXPRESSIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To add and subtract radicals, we need to be aware of like and unlike radicals.
Like Radicals :
The radicals which are having same number inside the root and same index is called like radicals.
Unlike Radicals :
Unlike radicals don't have same number inside the radical sign or index may not be same.
We can add and subtract like radicals only.
The following steps will be useful to simply radical expressions
Step 1 :
Decompose the number inside the radical sign into prime factors.
Step 2 :
Take one number out of the radical for every two same numbers multiplied inside the radical sign, if the radical is a square root.
Take one number out of the radical for every three same numbers multiplied inside the radical sign, if the radical is a cube root.
Step 3 :
Simplify.
Examples :
√4 = √(2 ⋅ 2) = 2
√16 = √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2) = 2 ⋅ 2 = 2
3√27 = 3√(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3) = 3
3√125 = 3√(5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5) = 5
Simplify the following radical expressions :
Example 1 :
√3 + √12
Solution :
= √3 + √12
= √3 + √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3)
= √3 + 2√3
= 3√3
Example 2 :
√75 + √25
Solution :
= √75 + √3
= √(5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 3) + √3
= 5√3 + √3
= 6√3
Example 3 :
√18 + √98
Solution :
= √18 + √98
= √(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2) + √(7 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 2)
= 3√2 + 7√2
= 10√2
Example 4 :
√5 + 2√5 - 5√5
Solution :
= √5 + √20 - √125
= √5 + √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 5) - √(5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5)
= √5 + 2√5 - 5√5
= -2√5
Example 5 :
√5 + 3√7 - 4√5 - 5√7
Solution :
√5 + 3√7 - 4√5 - 5√7
Group the like radicals.
= (√5 - 4√5) + (3√7 - 5√7)
Combine the like radicals.
= (-3√5) + (-2√7)
= -3√5 - 2√7
Example 6 :
3√3 + 4√3 - √2
Solution :
= 3√3 + 4√3 - √2
Group the like radicals.
= (3√3 + 4√3) - √2
Combine the like radicals.
= 7√3 - √2
Example 7 :
2(√5 - √3) + 3(√3 - √5)
Solution :
= 2(√5 - √3) + 3(√3 - √5)
Use Distributive Property.
= 2√5 - 2√3 + 3√3 - 3√5
Group the like radicals.
= (2√5 - 3√5) + (-2√3 + 3√3)
Combine the like radicals.
= -√5 + √3
Example 8 :
√8 + √18
Solution :
= √8 + √18
= √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2) + √(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2)
= 2√2 + 3√2
= 5√2
Example 9 :
3√16 + 3√54
Solution :
= 3√16 + 3√54
= 3√(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2) + 3√(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2)
= 23√2 + 33√2
= 53√2
Example 10 :
√25 + 53√64
Solution :
= √25 + 53√64
= √(5 ⋅ 5) + 53√(4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4)
= 5 + 5(4)
= 5 + 20
= 25
Example 11 :
√12w + √27w
Solution :
= √(12w) + √(27w)
= √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ w) + √(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ w)
= 2√3w + 3√3w
= 5√3w
Example 12 :
√45y3 + √25y3
Solution :
= √45y3 + √25y3
= √(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5 ⋅ y ⋅ y ⋅ y) + √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 5 ⋅ y ⋅ y ⋅ y)
= 3y√5y + 2y√5y
=5y√5y
= 5y√5y
Example 13 :
3√8x3y6 + √9x2y4
Solution :
= 3√8x3y6 + √9x2y4
= 3√(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ x ⋅ x ⋅ x ⋅ y2 ⋅ y2 ⋅ y2) + √(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ x ⋅ x ⋅ y2 ⋅ y2)
= 2xy2 + 3xy2
= 5xy2
Example 14 :
√4p2q4 - 3√125p3q6
Solution :
= √4p2q4 - 3√125p3q6
= √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ p ⋅ p ⋅ q2 ⋅ q2) - √(5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ p ⋅ p ⋅ p ⋅ q2 ⋅ q2 ⋅ q2)
= 2pq2 - 5pq2
= - 3pq2
Example 15 :
A square has sides each measuring 2√7 feet. Determine the area of the square.
Solution :
Side length of square = 2√7 feet
Area of square = Side x side
= 2√7 x 2√7
= 4 √7 x √7
= 4√(7x 7)
= 4 (7)
= 28 square feet
So, area of the square is 28 square feet.
Example 16 :
The period of a pendulum is the time required for it to make one complete swing back and forth. The formula of the period P of the pendulum is P = 2 π√(l/32), where l is the length of the pendulum in feet. If a pendulum in a clock tower is 8 feet long, find the period. Use 3.14 for π.
Solution :
P = 2 π√(l/32)
Here l = 8 feet
P = 2 x 3.14√(8/32)
= 2 x 3.14√(1/4)
= 2 x 3.14 √(1/2 x 2)
= 2 x 3.14 x 1/2
= 3.14 feet
So, the length of period is 3.14 feet.
Example 17 :
A rectangle has width 3√5 centimeters and length 4√10 centimeters. Find the area of the rectangle.
Solution :
Length = 4√10 cm
Width = 3√5 cm
Area of rectangle = length x width
= 4√10 x 3√5
= (4 x 3) √10 √5
= 12 √(5 x 2 x 5)
= 12 x 5√2
= 60 √2 cm2
Example 18 :
A rectangle has length √(a/8) meters and width √(a/2) meters. What is the area of the rectangle ?
Solution :
Length = √(a/8) meters
Width = √(a/2) meters
Area of rectangle = length x width
= √(a/8) x √(a/2)
= √(a/8) x (a/2)
= √(a x a) /(2 x 2 x 2 x 2)
= a/(2 x 2)
= a/4
So, area of the rectangle is a/4 square meter.
Example 19 :
The formula for the area A of the square with side length s is A = s2. Solve this equation for s, find the side length of a square having an area of 72 square units.
Solution :
A = s2
Area of square = 72 square units.
72 = s2
s = √72
s = √(6 x 6 x 2)
= 6 √2
So, the side length of the square is 6 √2 units.
Example 20 :
Find the area of the rectangle
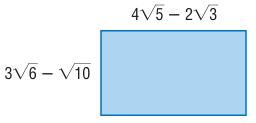
Solution :
Length = 4√5 - 2√3
Width = 3√6 - √10
Area of rectangle = length x width
= (4√5 - 2√3)(3√6 - √10)
= 4√5 (3√6) - 4√5(√10) - 2√3(3√6) - 2√3(√10)
= 12√30 - 4√(5 x 5 x 2) - 6√(3 x 3 x 2) - 2√30
= 12√30 - (4 x 5)√2 - (6 x 3)√2 - 2√30
= 12√30 - 20√2 - 18√2 - 2√30
= 18√30 - 38√2
So, the area of the rectangle is 18√30 - 38√2 square units.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


