GCD OF POLYNOMIALS USING DIVISION ALGORITHM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
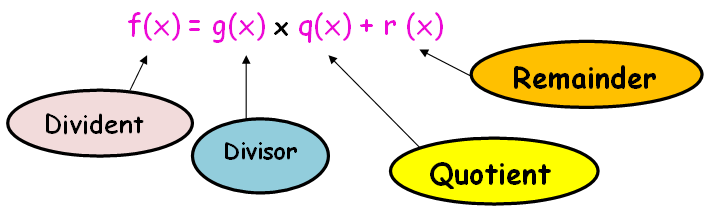
If f (x) and g(x) are two polynomials of same degree then the polynomial carrying the highest coefficient will be the dividend.
In case, if both have the same coefficient then compare the next least degree’s coefficient and proceed with the division.
If r (x) = 0 when f(x) is divided by g(x) then g(x) is called GCD of the polynomials.
Example 1 :
Find the GCD of the following polynomials.
x4 + 3x3 −x −3, x3 +x2 −5x + 3
Solution :
Let f(x) = x4 + 3x3 −x −3
g(x) = x3 +x2 −5x + 3
The degree of the polynomial f(x) is greater than g(x).
Note : If we have any missing term, we have to replace that place by 0.
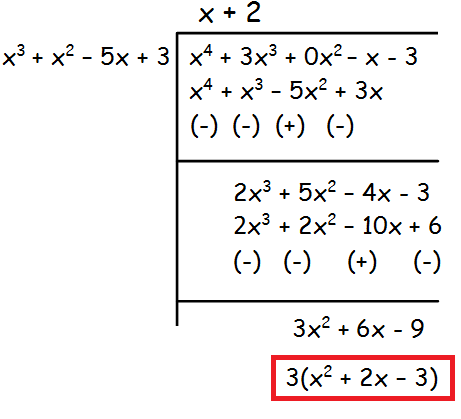
The remainder is 3(x2 + 2x - 3), which is not equal to 0.So, we have to divide x3 +x2 −5x + 3 by x2 + 2x - 3 by leaving the remainder.
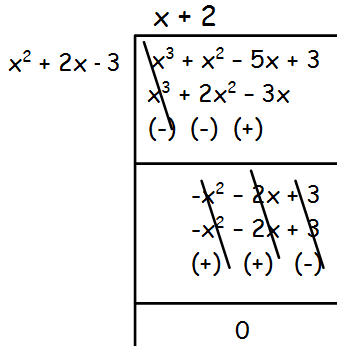
We get 0 as remainder by dividing the given polynomial by x2 + 2x - 3.
Hence the required GCD is x2 + 2x - 3.
Example 2 :
Find the GCD of the following polynomials.
x4 - 1, x3 - 11x2 + x - 11
Solution :
Let f(x) = x4 - 1
g(x) = x3 - 11x2 + x - 11
The degree of the polynomial f(x) is greater than g(x).
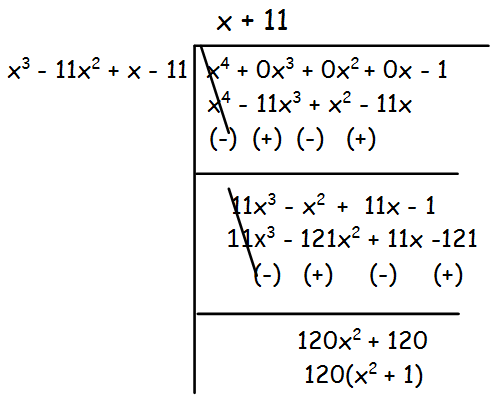
The remainder is 120(x2 + 1), which is not equal to 0.So, we have to divide x3 - 11x2 + x - 11 by 120(x2 + 1) by leaving the remainder.
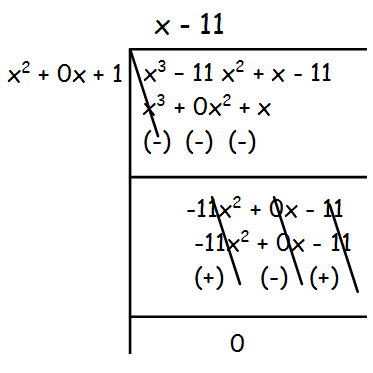
Hence the G.C.D is x2 + 1
Example 3 :
Find the GCD of the following polynomials.
3x4 + 6x3 −12x2 −24x, 4x4 +14x3 + 8x2 −8x
Solution :
Let f(x) = 3x4 + 6x3 −12x2 −24x
f(x) = 3x(x3 + 2x2 - 4x - 8)
g(x) = 4x4 +14x3 + 8x2 −8x
g(x) = 2x (x3 + 7x2 + 4x - 4)
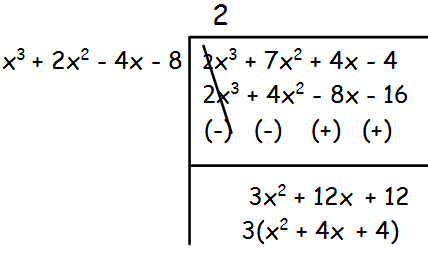
The remainder is 3(x2 + 4x + 4), which is not equal to 0.So, we have to divide x3 + 2x2 - 4x - 8 by x2 + 4x + 4 by leaving the remainder.
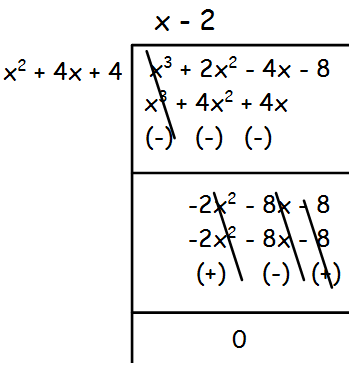
By dividing x2 + 4x + 4, we get 0 remainder. The term x is also common for both the polynomials.
Hence the G.C.D is x(x2 + 4x + 4).
Example 4 :
Find the GCD of the following polynomials.
3x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 3 , 6x3 +12x2 + 6x +12
Solution :
Let f(x) = 3x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 3
f(x) = 3(x3 + x2 + x + 1)
g(x) = 6x3 + 12x2 + 6x + 12
g(x) = 6(x3 + 2x2 + x + 2)

The remainder is (x2 + 0x + 1), which is not equal to 0.So, we have to divide x3 + x2 + x + 1 by x2 + 0x + 1 by leaving the remainder.
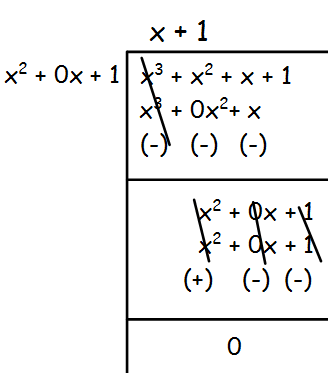
By dividing x2 + 1, we get 0 remainder. The constant 3 is also common for both the polynomials.
Hence the G.C.D is 3(x2 + 1).
Example 5 :
Find the HCF and LCM of the expressions x2 - 5x + 6 and x2 - 7x + 10 by factorization.
Solution :
x2 - 5x + 6 = x2 - 2x - 3x + 6
= x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2)
= (x - 2)(x - 3) -----(1)
x2 - 7x + 10 = x2 - 5x - 2x + 10
= x(x - 5) - 2(x - 5)
= (x - 2)(x - 5) -------(2)
Comparing (1) and (2)
HCF = x - 2
LCM = (x - 2)(x - 3)(x - 5)
Example 6 :
Find the HCF and LCM of the expressions (x + 3) (6x2 + 5x - 4) and (2x2 + 7x + 3)(x + 3) by factorization.
Solution :
(x + 3) (6x2 + 5x - 4)
= (x + 3) (6x2 + 8x - 3x - 4)
= (x + 3) [2x(3x + 4) - 1(3x + 4)]
= (x + 3) (2x - 1)(3x + 4) -------(1)
(2x2 + 7x + 3)(x + 3)
= (2x2 + 6x + 1x + 3)(x + 3)
= [2x(x + 3) + 1(x + 3)](x + 3)
= (2x + 1)(x + 3)(x + 3)
= (2x + 1)(x + 3)2 -------(2)
Comparing (1) and (2)
LCM = (x + 3)2 (2x - 1)(3x + 4)(2x + 1)
HCF = x + 3
Example 7 :
Find the HCF and LCM of the expressions
(x2 + xy + y2) and (x3 - y3)
Solution :
(x2 + xy + y2) and (x3 - y3)
= (x2 + xy + y2) ------(1)
The first expression cannot factorable.
x3 - y3 = (x - y)(x2 + xy + y2) ------(2)
Comparing (1) and (2)
LCM = (x2 + xy + y2) (x - y)
HCF = (x2 + xy + y2)
Example 8 :
Find the HCF and LCM of the expressions
(x2 - 9) and (x2 - 6x + 9)
Solution :
(x2 - 9) = x2 - 32
= (x - 3)(x + 3) ------(1)
x2 - 6x + 9 = x2 - 3x - 3x + 9
= [x(x - 3) - 3(x - 3)]
= (x - 3)(x - 3)
= (x - 3)2 ------(2)
Comparing (1) and (2)
LCM = (x - 3)2 (x + 3)
HCF = (x - 3)
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers
Feb 25, 26 08:07 AM
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers -
Solving Exponential Equations
Feb 23, 26 10:06 AM
Solving Exponential Equations - Concept - Examples -
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals