RATIONAL ROOT THEOREM
Ration Root (or Rational Zero) Theorem :
Suppose that all the coefficients of the polynomial function described by
p(x) = anxn + an–1xn–1 + ....................+ a2x2 + a1x + a0
are integers with an ≠ 0 and a0 ≠ 0. If p/q is a root of p(x) in lowest terms, then p is a factor of a0 and q is a factor of an.
Stated another way, the Rational-Root Theorem says that if a simple fraction in lowest terms (a rational number) is a root of a polynomial function with integer coefficients, then the numerator of the rational root is a factor of the constant term of the polynomial, and the denominator of the rational root is a factor of the leading coefficient of the polynomial.
Example 1 :
State the possible rational roots of f(x) and find all rational roots.
f(x) = 5x3 + 29x2 + 19x - 5
Solution :
The constant term is 5 and the leading coefficient is -5.
Factors of -5 : ±1, ±5.
Factors of 5 : ±1, ±5.
So, the possible rational roots are
±1/1, ±1/5, ±5/1, ±5/5
or
±1/1, ±1/5, ±5
Check 1 is rational root to f(x).
f(1) = 5(1)3 + 29(1)2 + 19(1) - 5
= 5 + 29 + 19 - 5
= 5 + 29 + 19 - 5
= 48 ≠ 0
Check -1 is rational root to f(x).
f(1) = 5(-1)3 + 29(-1)2 + 19(-1) - 5
= -5 + 29 - 19 - 5
= 0
Check 1/5 is rational root to f(x).
f(1/5) = 5(1/5)3 + 29(1/5)2 + 19(1/5) - 5
= 5(1/125) + 29(1/25) + 19/5 - 5
= 1/25 + 29/25 + 19/5 - 5
= 1/25 + 29/25 + 19/5 - 5
= 1/25 + 29/25 + 19/5 - 5
= 0
Check -1/5 is rational root to f(x).
f(1/5) = 5(-1/5)3 + 29(-1/5)2 + 19(-1/5) - 5
= 5(-1/125) - 29(1/25) - 19/5 - 5
= -1/25 - 29/25 - 19/5 - 5
= -1/25 + 29/25 + 19/5 - 5
= 1/25 + 29/25 + 19/5 - 5
= 98/25 ≠ 0
Check 5 is rational root to f(x).
f(5) = 5(5)3 + 29(5)2 + 19(5) - 5
= 625 + 725 + 95 - 5
= 1440 ≠ 0
Check -5 is rational root to f(x).
f(-5) = 5(-5)3 + 29(-5)2 + 19(-5) - 5
= -625 + 725 - 95 - 5
= 0
f(x) becomes zero when
x = -5, -1, 1/5
So, the rational roots of f(x) are -5, -1 and 1/5.
Example 2 :
Use the Rational-Root Theorem to find all rational roots of
f(x) = 4x4 + 3x3 + 4x2 + 11x + 6
Solution :
The constant term is +6 and the leading coefficient is 4.
Factors of 6 : ±1, ±2, ±3, ±6
Factors of 4 : ±1, ±2, ±4
The possible rational roots are
±1, ±2, ±3, ±6, ±1/2, ±3/2, ±1/4, ±3/4
There are sixteen possible rational roots. It's little hard to check each rational root with f(x) as we have done in the previous problem.
So, we can use the graph of the given function to find the actual rational roots.
The smallest possible rational root is –6 and the largest is 6, so graph f on the interval –6 ≤ x ≤ 6 to see where rational roots might be.
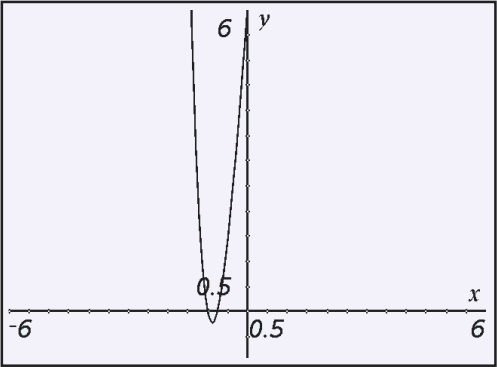
The graph above shows that there are two real roots on the interval –1 ≤ x ≤ 0.
Use a graphing utility to find the x-intercepts of the graph of f(x).
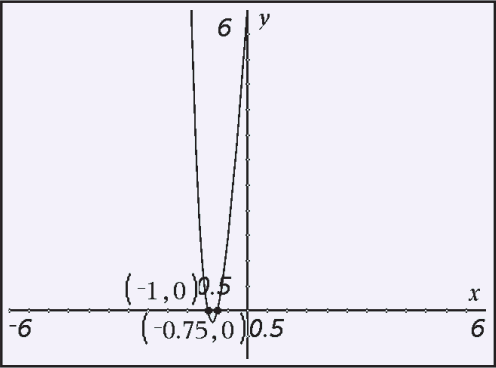
The possible rational roots in the interval –1 ≤ x ≤ 0 are
-1,-3/4, -1/2, -1/4
Test these values with f(x).
f(-1) = 0
f(-3/4) = 0
f(-1/2) ≈ 1.38
f(-1/4) ≈ 3.47
So, –1 and –3/4 are the only rational roots of f(x).
Note :
The Rational-Root Theorem identifies all possible rational roots of a
polynomial with integer coefficients. So, any real roots that are not
identified must be irrational.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle
Apr 26, 24 09:20 PM
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle - Concept - Solved Examples -
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Apr 26, 24 12:39 PM
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form or Vertex Form -
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials
Apr 26, 24 01:51 AM
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials - Key Concepts - Solved Problems