INTEGRATION USING PARTIAL FRACTIONS EXAMPLES
Integration Using Partial Fractions Examples :
Here we are going to see some example problems in integration using the concept of partial fractions.
Integration Using Partial Fractions Examples
Example 1 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2
Solution :
Decompose the given rational function into partial fractions.
1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2 = A/(x - 1) + B/(x + 2) + C/(x + 2)2
1 = A(x+2)2 + B(x-1)(x+2) + C(x-1)
Plug x = 1
1 = 9A
A = 1/9
Plug x = -2
1 = C(-3)
C = -1/3
Plug x = 0
1 = 4A-2B-C
1 = 4(1/9) - 2B - (-1/3)
1 = (4/9)- 2B + (1/3)
1 - (4/9) - (1/3) = -2B
-2B = (9 - 4 - 3)/9
-2B = 2/9
B = -1/9
Integrate.
∫[1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2] dx
= (1/9)∫(1/(x-1))dx-(1/9)∫(1/(x+2)-(1/3)∫(1/(x+2)2 dx
= (1/9)log(x-1) - (1/9)log (x+2)-(1/3)(1/(x+2)) + c
= (1/9) [log(x - 1) - log(x + 2)] - (1/3)(1/(x+2)) + c
= (1/9) [log(x - 1)/(x - 2)] - (1/3(x + 2)) + c
Example 2 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)
Solution :
Decompose the given rational function into partial fractions.
(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)
= A/(x - 1) + B/(x + 2) + (Cx + D)/(x2 + 1)
3x - 9 = A(x+2)(x2+1)+B(x-1)(x2+1)+(Cx+D)(x-1)(x+2)
Plug x = 1
3 - 9 = A(6)
-6 = 6A ==> A = -1
Plug x = -2
-6 - 9 = B(-3)(5)
-15 = -15B ==> B = 1
Plug x = 0
- 9 = 2A - B - 2D
-9 = 2(-1) - 1 - 2D
-9 + 3 = -2D
-6 = -2D
D = 3
3x - 9 = A(x+2)(x2+1)+B(x-1)(x2+1)+(Cx+D)(x-1)(x+2)
Plug x = -1
- 12 = A(1)(2) + B(-2)(2) + (-C+D)(-2)
-12 = 2A - 4B + 2C - 2D
-12 = 2(-1) - 4(1) + 2C - 2(3)
-12 = -2 - 4 - 6 + 2C
2C = -12 + 12
C = 0
Integrate.
∫[(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)] dx
= -∫1/(x - 1) dx + ∫1/(x + 2) dx + ∫ 3/(x2 + 1) dx
= - log (x - 1) + log (x + 2) + 3 tan-1(x)
= log (x + 2)/(x - 1) + 3 tan-1(x) + c
Example 3 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2)
Solution :
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = x3/(x2 - 3x + 2)
In the given rational fraction, the highest exponent of x in numerator is greater than the highest exponent of x in denominator.
So, we can use long division to decompose the given rational function.
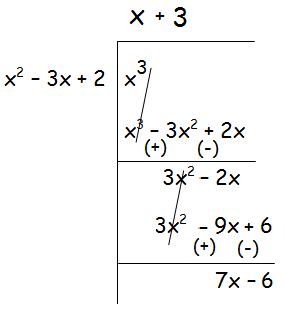
From the above long division, we have
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) + (7x - 6)/(x2 - 3x + 2)
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) + (7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) ----(1)
Decompose (7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) into partial fractions.
(7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) = A/(x - 1) + B(x - 2)
Simplify.
7x - 6 = A(x - 2) + B(x - 1)
Plug x = 1
7(1) - 6 = A(1 -2 ) + B(1 - 1)
1 = A(-1)
A = -1
Plug x = 2
7(2) - 6 = A(2 -2 ) + B(2 - 1)
8 = B(1)
B = 8
Therefore we have
(1)-----> x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) - 1/(x - 1) + 8/(x - 2)
Integrate.
∫[x3/(x - 1)(x - 2)] dx
= ∫(x + 3) dx -∫1/(x - 1) dx + 8∫1/(x - 2) dx
= x2/2 + 3x - log(x - 1) + 8log(x - 2) + C

After having gone through the stuff given above, we hope that the students would have understood, how to integrate rational functions using partial fractions.
Apart from the stuff given in this section, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle
Apr 26, 24 09:20 PM
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle - Concept - Solved Examples -
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Apr 26, 24 12:39 PM
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form or Vertex Form -
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials
Apr 26, 24 01:51 AM
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials - Key Concepts - Solved Problems