NATURE OF THE ROOTS OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
In this section, we will examine the roots of a quadratic equation.
That is, we will analyze whether the roots of a quadratic equation are equal or unequal, real or imaginary and rational or irrational.
To examine the roots of a quadratic equation, let us consider the general form a quadratic equation.
ax2 + bx + c = 0
(Here a, b and c are real and rational numbers)
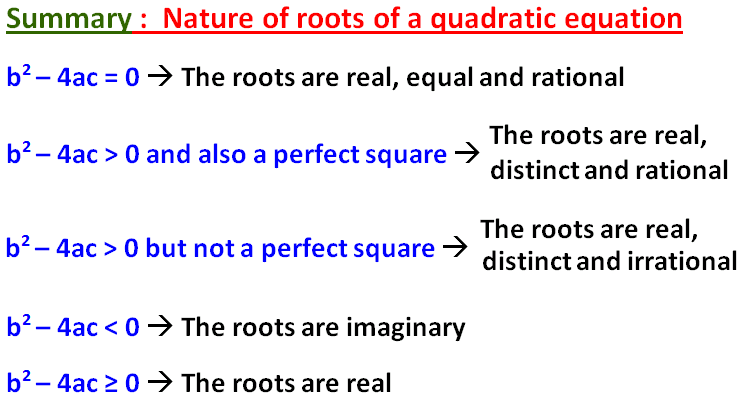
To know the nature of the roots of a quadratic-equation, we will be using the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
Because b2 - 4ac discriminates the nature of the roots.
Let us see how this discriminant b2 - 4ac can be used to know the nature of the roots of a quadratic-equation.

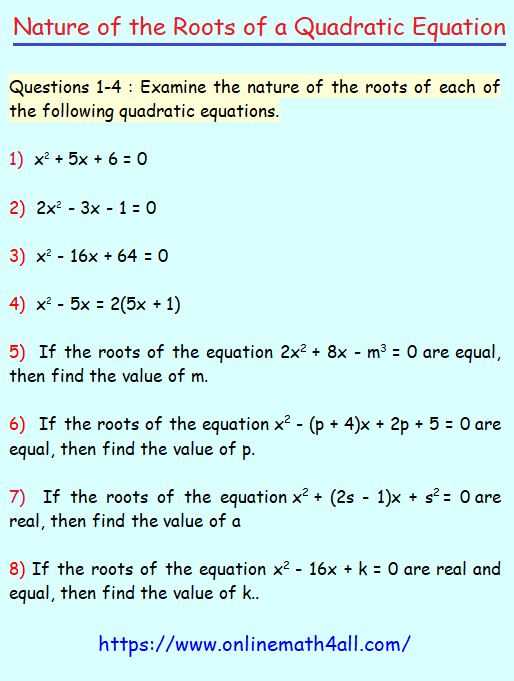
Examples 1-4 : Examine the nature of the roots of each of the following quadratic equations.
Example 1 :
8x2 - 7x - 1 = 0
Solution :
The given quadratic equation is in general form.
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and 8x2 - 7x - 1 = 0,
a = 8, b = -7, c = -1
Find the value of the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
b2 - 4ac = (-7)2 - 4(8)(-1)
= 49 + 32
= 81
or
= 92
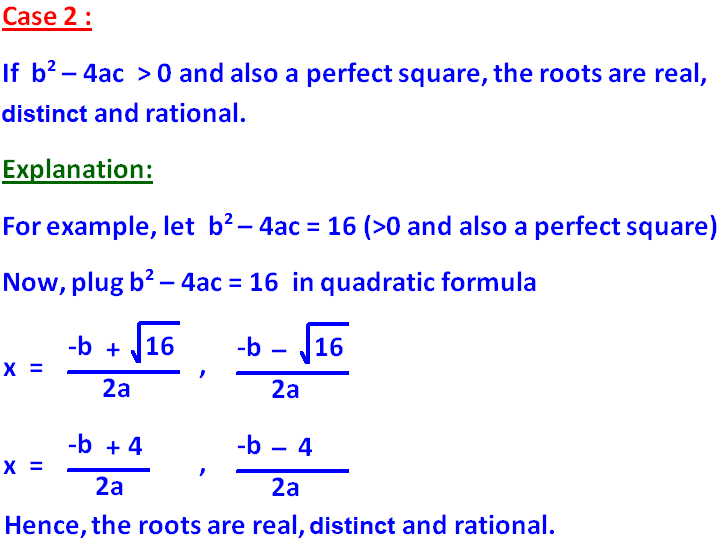
b2 - 4ac = 81 > 0 and also a perfect square.
So, the roots are real, unequal and rational.
Example 2 :
x2 - 3x - 1 = 0
Solution :
The given quadratic equation is in general form
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and x2 - 3x - 1 = 0,
a = 1, b = -3, c = -1
Find the value of the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
b2 - 4ac = (-3)2 - 4(1)(-1)
= 9 + 4
= 13
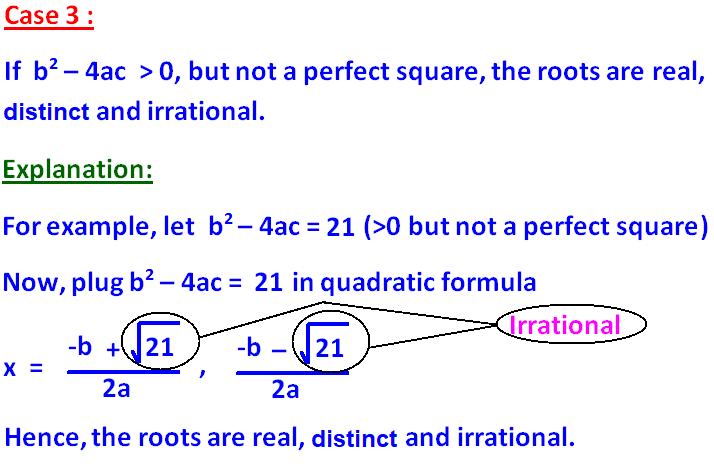
Here, b2 - 4ac = 13 > 0, but not a perfect square.
So, the roots are real, unequal and irrational.
Example 3 :
x2 - 26x + 169 = 0
Solution :
The given quadratic equation is in general form.
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and x2 - 3x - 1 = 0,
a = 1, b = -26, c = 169
Find the value of the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
b2 - 4ac = (-26)2 - 4(1)(169)
= 676 - 676
= 0
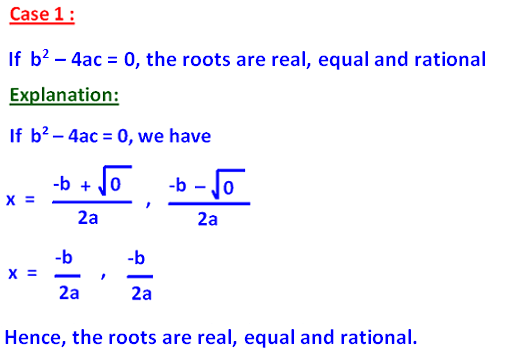
Since b2 - 4ac = 0, the roots are real, equal and rational.
Example 4 :
¹⁄₍ₓ ₋ ₇₎ + ³⁄₍ₓ ₊ ₄₎ = 1
Solution :
The given quadratic equation is not in general form.
Writing the given quadratic equation in general form :
¹⁄₍ₓ ₋ ₇₎ + ³⁄₍ₓ ₊ ₄₎ = 1
Multiply both sides of the equation by (x - 7)(x + 4) to get rid of the denominators on the left side.
(x - 7)(x + 4)(¹⁄₍ₓ ₋ ₇₎ + ³⁄₍ₓ ₊ ₄₎) = 1(x - 7)(x + 4)
Using Distributive Property,
(x + 4) + 3(x - 7) = (x - 7)(x + 4)
x + 4 + 3x - 21 = x2 - 3x - 28
4x - 17 = x2 - 3x - 28
0 = x2 - 7x - 11
or
x2 - 7x - 11 = 0
Now, the quadratic equation is in general form
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and x2 - 7x - 11 = 0,
a = 1, b = -7, c = -11
Find the value of the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
b2 - 4ac = (-7)2 - 4(1)(-11)
= 49 + 44
= 93
Here, b2 - 4ac > 0, but not a perfect square.
So, the roots are real, unequal and irrational.
Example 5 :
9x2 - 6x + k = 0
If the roots of the above quadratic equation are real, equal and rational, find the value of k.
Solution :
The given quadratic equation is in general form
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and 9x2 - 6x + k = 0,
a = 9, b = -6, c = k
Since the roots are real, equal and rational, the value of the discriminant 'b2 - 4ac' must be zero.
b2 - 4ac = 0
Substitute a = 9, b = 6 and c = k.
62 - 4(9)k = 0
36 - 36k = 0
Subtract 36 from both sides.
-36k = -36
Divide both sides by -36.
k = 1
Example 6 :
6x = 2 - y
y = x2 + 11
Find the number ordered pairs (x, y) in the xy-plane are solutions to the system of equations above?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) Infinitely Many
Solution :
6x = 2 - y ----(1)
y = x2 + 11 ----(2)
In (1), solve for y in terms of x.
6x = 2 - y
Add y to both sides.
6x + y = 2
Subtract 6x from both sides.
y = 2 - 6x
Multiply both sides by 2.
y = 2 - 6x
Substitute y = 2 - 6x in (2).
2 - 6x = x2 + 11
x2 + 6x + 9 = 0
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and x2 + 6x + 9 = 0,
a = 1, b = 6 and c = 9
Find the value of the discriminant b2 - 4ac.
b2 - 4ac = 92 - 4(1)(8)
b2 - 4ac = 81 - 32
b2 - 4ac = 49
Since b2 - 4ac = 49 > 0, the roots are real and unequal. It means, there are real values for x. Hence, there will be two real values for y.
Therefore, two ordered pairs in the xy-plane are solutions to the given system of equations.
The correct answer choice is (C).
Example 7 :
3x2 - 6x + m = 0
If the quadratic equation above has two real roots, find all possible values of m.
Solution :
Comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 and 3x2 - 6x + m = 0,
a = 3, b = -6 and c = m
Since the given quadratic has two real roots, the value of the discriminant 'b2 - 4ac' must be greater than zero.
b2 - 4ac > 0
(-6)2 - 4(3)(m) > 0
36 - 12m > 0
Subtract 36 from both sides.
-12m > -36
Divide both sides by -12.
m < 3
Any real value less than 3 can be the value of m.
Click here to get detailed answers for the above questions.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 46)
Jan 27, 26 07:05 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 46) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 45)
Jan 19, 26 06:14 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 45) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)
Jan 12, 26 06:35 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)