FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION
A frequency distribution may be defined as a tabular representation of statistical data, usually in an ascending order, relating to a measurable characteristic according to individual value or a group of values of the characteristic under study.
The following steps would be useful to construct a frequency distribution.
Step 1 :
Find the largest and smallest observations and obtain the difference between them, known as Range, in case of a continuous variable.
Step 2 :
Form a number of classes depending on the number of isolated values assumed by a discrete variable. In case of a continuous variable, find the number of class intervals using the relation,
No. of class Interval X class length ≅ Range.
Step 3 :
Present the class or class interval in a table known as frequency-distribution table.
Step 4 :
Apply ‘tally mark’ i.e. a stroke against the occurrence of a particulars value in a class or class interval.
Step 5 :
Count the tally marks and present these numbers in the next column, known as frequency column, and finally check whether the total of all these class frequencies tally with the total number of observations.
Example 1 :
Following are the records of babies born in an hospital in San Francisco during a week (B denoting Boy and G for Girl) :
B G G B G G B B G G
G G B B B G B B G B
B B G B B B G G B G
Construct a frequency distribution according to gender.
Solution :
In order to construct a frequency distribution of babies in accordance with their gender, we count the number of male births and that of female births and present this information in the following table.
|
Category Boy (B) Girl (G) Total |
Number of births 16 14 30 |
Example 2 :
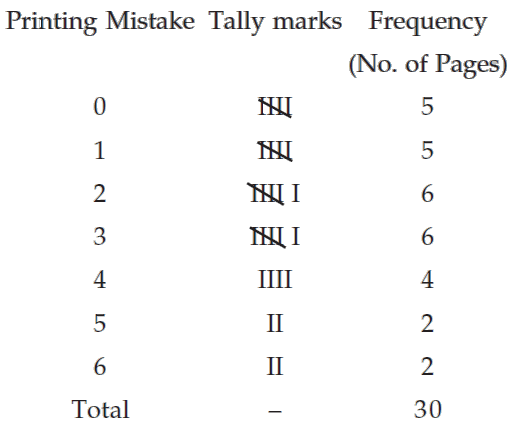
A review of the first 30 pages of a statistics book reveals the following printing mistakes :
0 1 3 3 2 5 6 0 1 0
4 1 1 0 2 3 2 5 0 4
2 3 2 2 3 3 4 6 1 4
Make a frequency distribution of printing mistakes.
Solution :
Since x, the printing mistakes, is a discrete variable, x can assume seven values 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Thus we have 7 classes, each class comprising a single value.
Frequency distribution of the number of printing mistakes of the first 30 pages of a book
Example 3 :
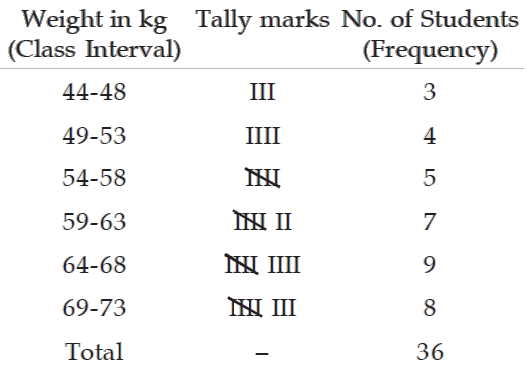
Following are the weights in kgs. of 36 students of an university.
70 73 49 61 61 47 57 50 59
59 68 45 55 65 68 56 68 55
70 70 57 44 69 73 64 49 63
65 70 65 62 64 73 67 60 50
Construct a frequency distribution of weights, taking class length as 5.
Solution :
Range = Maximum weight – minimum weight
= 73 – 44
= 29 kgs
No. of class interval x class length ≅ Range
No. of class interval x 5 ≅ 29
No. of class interval ≅ ²⁹⁄₅
No. of class interval ≅ 6
(We always take the next integer as the number of class intervals so as to include both the minimum and maximum values)
Frequency distribution of weights of 36 Students
Important Notes
In case, the characteristic under consideration is an attribute, say nationality, then the tabulation is made by allotting numerical figures to the different classes the attribute may belong like, in this illustration, counting the number of American, Indian, British, French, German and so on.
The qualitative characteristic is divided into a number of categories or classes which are mutually exclusive and exhaustive and the figures against all these classes are recorded.
The figure corresponding to a particular class, signifying the number of times or how frequently a particular class occurs is known as the frequency of that class.
Thus,
the number of Americans, as found from the given data, signifies the
frequency of the Americans. So frequency distribution is a statistical
table that distributes the total frequency to a number of classes.
When tabulation is done in respect of a discrete random variable, it is known as Discrete or Un grouped or simple Frequency Distribution and in case the characteristic under consideration is a continuous variable, such a classification is termed as Grouped Frequency- distribution.
In case of a grouped frequency distribution, tabulation is done not against a single value as in the case of an attribute or a discrete random variable but against a group of values.
The distribution of the number of car accidents in New York during 12 months of the year 2005 is an example of a un grouped frequency distribution and the distribution of heights of the students of St. Xavier’s College for the year 2004 is an example of a grouped frequency-distribution.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Printable Math Worksheets
Apr 20, 24 12:02 AM
Printable Math Worksheets - Worksheets in Pdf formats from grade 1 to 10 -
Printable Math Worksheets for Grade 2
Apr 19, 24 11:58 PM
Printable Math Worksheets for Grade 2 -
Sequences and Series
Apr 19, 24 11:45 PM
Sequences and Series - Concept - Examples