DIRECT VARIATION
A direct variation is a special type of linear relationship that can be written in the form y = kx, where k is a nonzero constant called the constant of variation.
A recipe for paella calls for 1 cup of rice to make 5 servings. In other words, a chef needs 1 cup of rice for every 5 servings.
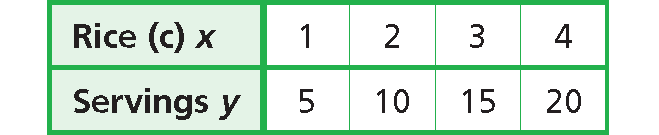
The equation y = 5x describes this relationship. In this relationship, the number of servings varies directly with the number of cups of rice.
Identifying Direct Variations from Equations
Tell whether each equation represents a direct variation. If so, identify the constant of variation.
Example 1 :
y = 4x
Solution :
This equation represents a direct variation, because it is in the form y = kx. The constant of variation is 4.
Example 2 :
-2x + 3y = 0
Solution :
-2x + 3y = 0
Solve the equation for y.
Because -2x is added to 3y, add 2x to each side.
3y = 2x
Because y is multiplied by 3, divide each side by 3.
3y/3 = 2x/3
y = (2/3)x
This equation represents a direct variation, because it can be written in the form y = kx. The constant of variation is 2/3.
Example 3 :
3x + 2y = 6
Solution :
3x + 2y = 6
Solve the equation for y.
Because 3x is added to 2y, subtract 3x from each side.
2y = -3x + 6
Because y is multiplied by 2, divide each side by 2.
2y/2 = (-3x + 6)/2
y = -3x/2 + 6/2
y = -3x/2 + 3
This equation does not represent a direct variation, because it cannot be written in the form y = kx.
What happens if you solve y = kx for k?
y = kx
Divide each side by x (x ≠ 0).
y/x = kx/x
y/x = k
So, in a direct variation, the ratio y/x is equal to the constant of variation. Another way to identify a direct variation is to check whether y/x is the same for each ordered pair (except where x = 0)
Identifying Direct Variations from Ordered Pairs
Tell whether each relationship is a direct variation. Explain.
Example 4 :
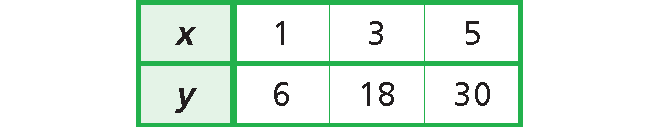
Solution :
Write an equation that represents the relationship given in the table above.
y = 6x
Each y-value is 6 times the corresponding x-value.
This is a direct variation.
Because the equation y = 6x is in the form of y = kx, where k = 6.
Example 5 :
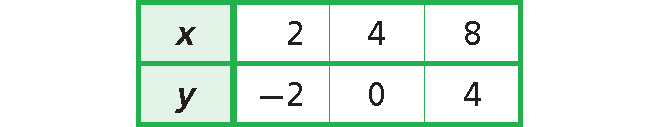
Solution :
Write an equation that represents the relationship given in the table above.
y = x - 4
Each y-value is 4 less than the corresponding x-value.
This is a not direct variation.
Because the equation y = x - 1 is not in the form of y = kx.
Writing and Solving Direct Variation Equations
Example 6 :
The value of y varies directly with x, and y = 8 when x = 2. Find y when x = 5.
Solution :
It is given that y varies directly with x.
Write the equation for a direct variation.
y = kx
Substitute 8 for y and 2 for x.
8 = k(2)
8 = 2k
Divide each side by 2.
8/2 = 2k/2
4 = k
The equation is
y = 4x
Find y, when x = 5.
y = 4(5)
y = 20
Graphing Direct Variations
Example 7 :
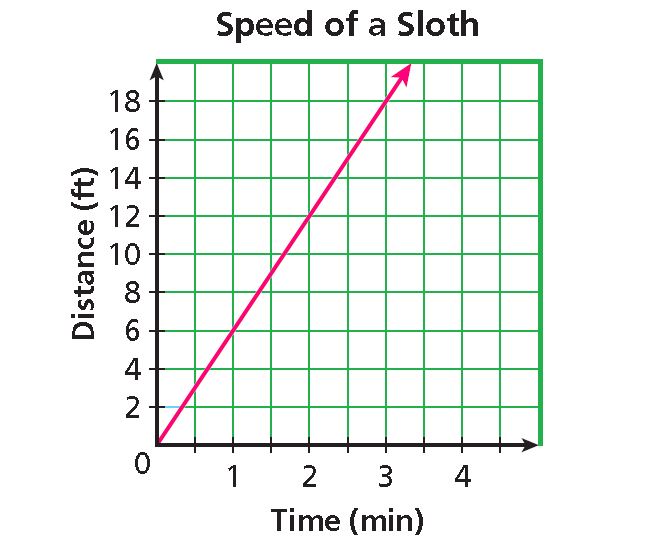
The three-toed sloth is an extremely slow animal. On the ground, it travels at a speed of about 6 feet per minute. Write a direct variation equation for the distance y a sloth will travel in x minutes. Then graph.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write a direct variation equation.
Distance
is
6 feet per minute
times
number of minutes
y
=
6
⋅
x
Step 2 :
Choose values of x and generate ordered pairs.
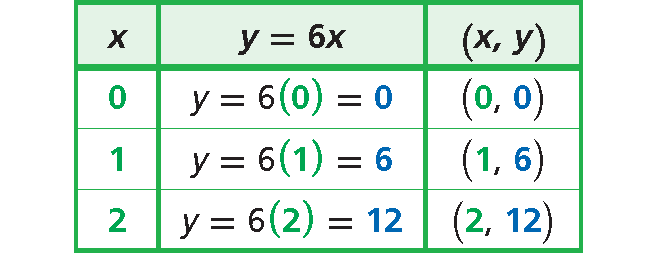
Step 3 :
Graph the points and connect.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 213)
Jul 13, 25 09:51 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 213) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 212)
Jul 13, 25 09:32 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 212) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 211)
Jul 11, 25 08:34 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 211)